Crafted with Care: The Artisanal Process Behind Our Frangipani Perfume
Frangipani: The Enchanting Elixir of Nature
In the realm of fragrances, few scents can rival the intoxicating allure of Frangipani. Also known as Plumeria, this tropical flower has captured the hearts of perfumers, aromatherapists, and nature enthusiasts alike. Its sweet, floral aroma and therapeutic properties have earned it a place in perfumes, therapeutic oils, and even traditional medicine. Join us on a journey to explore the enchanting world of Frangipani, uncovering its fragrance secrets, culinary potential, medicinal uses, fascinating history, and fun crazy facts.
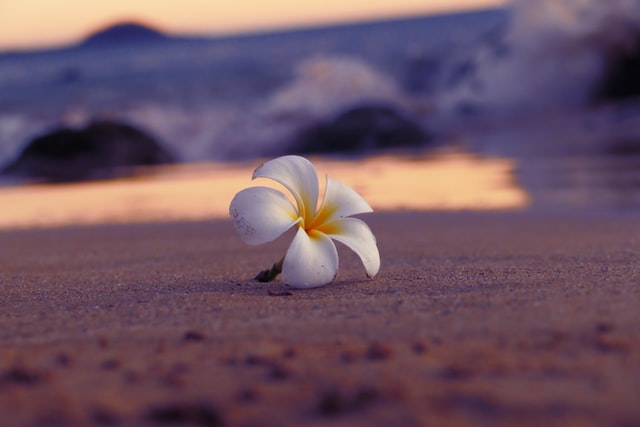
1. Introduction to Frangipani: Frangipani, scientifically known as Plumeria, is a genus of flowering plants native to tropical regions, including Central America, the Caribbean, and various parts of Southeast Asia. The plant features clusters of fragrant, waxy flowers with hues ranging from white and yellow to pink and red. Its name pays homage to the Italian nobleman, Marquis Frangipani, who crafted a perfume with a similar scent in the 16th century.
2. Perfumes and Fragrance: Frangipani's mesmerizing fragrance has found its way into numerous perfumes and fragrances. Its sweet and floral notes evoke feelings of joy, romance, and sensuality. Perfumers often blend Frangipani with other floral scents or infuse it with exotic spices to create luxurious and captivating fragrances.
3. Therapeutic Oils and Aromatherapy: In aromatherapy, Frangipani essential oil is cherished for its uplifting and mood-enhancing properties. The oil is believed to promote relaxation, ease stress, and elevate one's spirits. Aromatherapists often use Frangipani oil in diffusers, massage blends, and bath products to induce a sense of tranquility and emotional balance.
4. Culinary Potential: While Frangipani is not typically used in culinary practices due to its toxic properties, some cultures incorporate its essence in traditional drinks and desserts. However, it is essential to exercise caution when experimenting with Frangipani in food, as certain parts of the plant are poisonous if ingested.
5. Medicinal Uses: In traditional medicine, various parts of the Frangipani plant have been used to treat ailments ranging from skin conditions to respiratory issues. However, it is crucial to note that the plant contains toxic compounds and should only be used under the guidance of trained herbalists or healthcare practitioners.
6. History and Cultural Significance: Frangipani has deep cultural significance in many regions where it flourishes. In Hindu and Buddhist traditions, the flower holds spiritual significance and is often used in religious ceremonies and rituals. In Hawaiian culture, Frangipani symbolizes positivity, grace, and the welcoming spirit of the islands.
7. Fun and Crazy Facts: Frangipani's mesmerizing aroma has inspired numerous legends and myths across cultures. In some regions, the scent of Frangipani is associated with ghosts or otherworldly beings, adding to its mystique and allure.
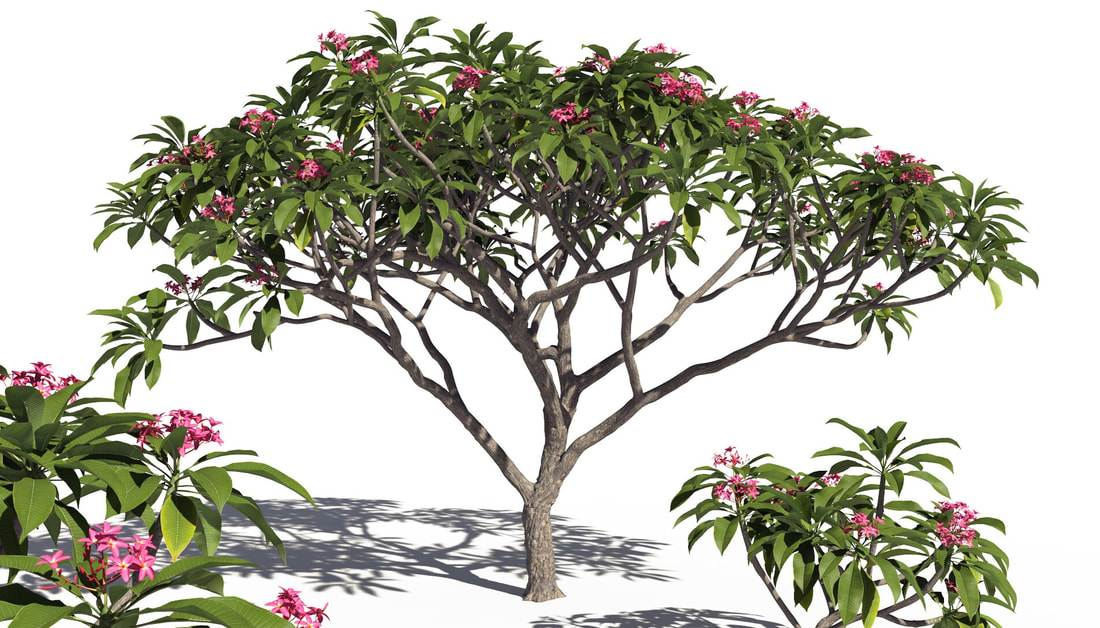
8. Varieties and Cultivation: The Frangipani genus boasts a wide range of varieties and cultivars, each with its unique characteristics and color variations. The plant is relatively easy to grow in warm, tropical climates and can be cultivated in home gardens, adding a touch of exotic elegance to the landscape.
9. Conservation and Preservation: Frangipani, like many other tropical flowers, faces threats from deforestation and urbanization. Conservation efforts are vital to protect this captivating flower and preserve its natural habitat for future generations to enjoy.
10. Frangipani in Literature and Art: Throughout history, Frangipani has inspired artists, poets, and writers. Its delicate beauty and intoxicating fragrance have been immortalized in literature, paintings, and other forms of artistic expression.
Frangipani, the enchanting elixir of nature, continues to captivate hearts and senses with its sweet, floral aroma and therapeutic properties. From perfumes and aromatherapy to its cultural significance and historical anecdotes, this tropical flower leaves an indelible mark on the world of fragrances and beyond. As we delve into its fragrant secrets and explore its various uses, let us remember to admire, cherish, and protect this mesmerizing bloom that brings joy and beauty to our lives.
In the realm of fragrances, few scents can rival the intoxicating allure of Frangipani. Also known as Plumeria, this tropical flower has captured the hearts of perfumers, aromatherapists, and nature enthusiasts alike. Its sweet, floral aroma and therapeutic properties have earned it a place in perfumes, therapeutic oils, and even traditional medicine. Join us on a journey to explore the enchanting world of Frangipani, uncovering its fragrance secrets, culinary potential, medicinal uses, fascinating history, and fun crazy facts.
1. Introduction to Frangipani: Frangipani, scientifically known as Plumeria, is a genus of flowering plants native to tropical regions, including Central America, the Caribbean, and various parts of Southeast Asia. The plant features clusters of fragrant, waxy flowers with hues ranging from white and yellow to pink and red. Its name pays homage to the Italian nobleman, Marquis Frangipani, who crafted a perfume with a similar scent in the 16th century.
2. Perfumes and Fragrance: Frangipani's mesmerizing fragrance has found its way into numerous perfumes and fragrances. Its sweet and floral notes evoke feelings of joy, romance, and sensuality. Perfumers often blend Frangipani with other floral scents or infuse it with exotic spices to create luxurious and captivating fragrances.
3. Therapeutic Oils and Aromatherapy: In aromatherapy, Frangipani essential oil is cherished for its uplifting and mood-enhancing properties. The oil is believed to promote relaxation, ease stress, and elevate one's spirits. Aromatherapists often use Frangipani oil in diffusers, massage blends, and bath products to induce a sense of tranquility and emotional balance.
4. Culinary Potential: While Frangipani is not typically used in culinary practices due to its toxic properties, some cultures incorporate its essence in traditional drinks and desserts. However, it is essential to exercise caution when experimenting with Frangipani in food, as certain parts of the plant are poisonous if ingested.
5. Medicinal Uses: In traditional medicine, various parts of the Frangipani plant have been used to treat ailments ranging from skin conditions to respiratory issues. However, it is crucial to note that the plant contains toxic compounds and should only be used under the guidance of trained herbalists or healthcare practitioners.
6. History and Cultural Significance: Frangipani has deep cultural significance in many regions where it flourishes. In Hindu and Buddhist traditions, the flower holds spiritual significance and is often used in religious ceremonies and rituals. In Hawaiian culture, Frangipani symbolizes positivity, grace, and the welcoming spirit of the islands.
7. Fun and Crazy Facts: Frangipani's mesmerizing aroma has inspired numerous legends and myths across cultures. In some regions, the scent of Frangipani is associated with ghosts or otherworldly beings, adding to its mystique and allure.
8. Varieties and Cultivation: The Frangipani genus boasts a wide range of varieties and cultivars, each with its unique characteristics and color variations. The plant is relatively easy to grow in warm, tropical climates and can be cultivated in home gardens, adding a touch of exotic elegance to the landscape.
9. Conservation and Preservation: Frangipani, like many other tropical flowers, faces threats from deforestation and urbanization. Conservation efforts are vital to protect this captivating flower and preserve its natural habitat for future generations to enjoy.
10. Frangipani in Literature and Art: Throughout history, Frangipani has inspired artists, poets, and writers. Its delicate beauty and intoxicating fragrance have been immortalized in literature, paintings, and other forms of artistic expression.
Frangipani, the enchanting elixir of nature, continues to captivate hearts and senses with its sweet, floral aroma and therapeutic properties. From perfumes and aromatherapy to its cultural significance and historical anecdotes, this tropical flower leaves an indelible mark on the world of fragrances and beyond. As we delve into its fragrant secrets and explore its various uses, let us remember to admire, cherish, and protect this mesmerizing bloom that brings joy and beauty to our lives.
To experience augmented reality, please open the Facebook-app using QR code and point to the image below
Plumeria flowers are most fragrant at night in order to lure sphinx moths to pollinate them. The flowers yield no nectar, however, and simply trick their pollinators.
A Fragrant Souvenir: Take Sentosa's Scent Home with You
Plant is named after 17th century French botanist Charles Plumier, who documented many plant and animal species of the new world. The common name "frangipani" comes from a 16th-century marquis of the noble family in Italy who claimed to invent a plumeria-scented perfume, but in reality made a synthetic perfume that was said at the time to resemble the odor of the recently discovered flowers. The name comes from frangi "breaking" + pani "bread," a reference to the family's distribution of bread in time of famine.
In eastern India, it is traditionally considered as a variety of champak flower, the golok chapa, meaning the champaka from Sree Krishna's home in heaven. This flower is considered sacred and also adorned by the name of gulancha and kath golap (literally, wood rose)
Frangipani (Plumeria) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. They are native to tropical regions of Central America, the Caribbean, and Mexico, and are widely cultivated as ornamental plants in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. The genus includes around 7-8 species, with the most well-known species being Plumeria rubra, which is widely cultivated for its fragrant, brightly colored flowers.
Frangipani plants are known for their large, fragrant flowers that bloom in a variety of colors, including white, pink, yellow, and red. The flowers are often used in traditional floral arrangements and are a popular subject in Asian art. The leaves are glossy and usually arranged spirally. The tree can grow up to 30 feet tall depending on the species.
Frangipani is also known for its medicinal properties, particularly the flowers and the sap. They are used to treat a variety of ailments, including fever, skin disorders and headaches. In many cultures, frangipani is associated with spiritual and mystical properties. They are often planted near temples and other religious sites.
Frangipani is also known for its ability to attract a variety of wildlife, including birds, bats and butterflies. The wood of the Frangipani tree is also used for construction, furniture and flooring.
In eastern India, it is traditionally considered as a variety of champak flower, the golok chapa, meaning the champaka from Sree Krishna's home in heaven. This flower is considered sacred and also adorned by the name of gulancha and kath golap (literally, wood rose)
Frangipani (Plumeria) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. They are native to tropical regions of Central America, the Caribbean, and Mexico, and are widely cultivated as ornamental plants in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. The genus includes around 7-8 species, with the most well-known species being Plumeria rubra, which is widely cultivated for its fragrant, brightly colored flowers.
Frangipani plants are known for their large, fragrant flowers that bloom in a variety of colors, including white, pink, yellow, and red. The flowers are often used in traditional floral arrangements and are a popular subject in Asian art. The leaves are glossy and usually arranged spirally. The tree can grow up to 30 feet tall depending on the species.
Frangipani is also known for its medicinal properties, particularly the flowers and the sap. They are used to treat a variety of ailments, including fever, skin disorders and headaches. In many cultures, frangipani is associated with spiritual and mystical properties. They are often planted near temples and other religious sites.
Frangipani is also known for its ability to attract a variety of wildlife, including birds, bats and butterflies. The wood of the Frangipani tree is also used for construction, furniture and flooring.
Unveiling the Secrets of Frangipani: A Fragrance as Unique as Sentosa
In Mesoamerica, plumerias have high significance for over two millennia, from the Maya and Aztec periods into the present. Among the Maya, plumerias have been associated with deities representing life and fertility, and the flowers also are connected with female sexuality. Nahuatl-speaking people during the height of the Aztec Empire used plumerias to signify elite status, and planted plumeria trees in the gardens of nobles.
In several Pacific islands, such as Tahiti, Fiji, Samoa, Hawaii, New Zealand, Tonga, and the Cook Islands plumeria species are used for making leis.
Frangipani was likely introduced to the island by Sir Stamford Raffles or by botanists and horticulturists during the early colonial period. Sir Stamford Raffles was a British statesman, administrator, and founder of modern Singapore, he is known for his interest in natural history and botany, and it is likely that he brought a variety of plant species to Singapore during his tenure as governor of the colony.
Frangipani became popular in Singapore as an ornamental plant because of its brightly colored, fragrant flowers and its ability to thrive in the tropical climate. It was often planted in gardens, parks, and along streets as a decorative tree. Frangipani also holds a special place in Singapore's cultural heritage, it is associated with spiritual and mystical properties and is often planted near temples and other religious sites.
The Frangipani flowers are also commonly used in traditional floral arrangements, and are a popular subject in Asian art. It is also used in perfumes and aromatherapy.
It should be noted that although Frangipani is often associated with Sir Stamford Raffles, it is not clear if he had any direct involvement in introducing the plant to Singapore or not.
In several Pacific islands, such as Tahiti, Fiji, Samoa, Hawaii, New Zealand, Tonga, and the Cook Islands plumeria species are used for making leis.
Frangipani was likely introduced to the island by Sir Stamford Raffles or by botanists and horticulturists during the early colonial period. Sir Stamford Raffles was a British statesman, administrator, and founder of modern Singapore, he is known for his interest in natural history and botany, and it is likely that he brought a variety of plant species to Singapore during his tenure as governor of the colony.
Frangipani became popular in Singapore as an ornamental plant because of its brightly colored, fragrant flowers and its ability to thrive in the tropical climate. It was often planted in gardens, parks, and along streets as a decorative tree. Frangipani also holds a special place in Singapore's cultural heritage, it is associated with spiritual and mystical properties and is often planted near temples and other religious sites.
The Frangipani flowers are also commonly used in traditional floral arrangements, and are a popular subject in Asian art. It is also used in perfumes and aromatherapy.
It should be noted that although Frangipani is often associated with Sir Stamford Raffles, it is not clear if he had any direct involvement in introducing the plant to Singapore or not.
Crafting Captivating Scents: Our Process of Perfume Artisanship
In Bengali culture, most white flowers, and in particular, plumeria (Bengali, chômpa or chãpa), are associated with funerals and death. Also in the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia, the plumeria is often associated with ghosts and cemeteries. Plumerias often are planted on burial grounds in all three nations.
Frangipani fun facts
Frangipani fun facts
- Frangipani flowers are edible and are used in culinary dishes in some cultures. They can be used to make tea, jelly and added as a flavoring to desserts.
- Frangipani is also known as "Temple Tree" or "West Indian Jasmine" because it was often planted near temples in India, and its flowers have a similar scent to the Jasmine flower.
- Frangipani is the national flower of Laos, where it is known as "Dok Champa" and is considered a symbol of good luck.
- In Hawaiian culture, Frangipani is known as "Melia" and is associated with the goddess of canoe builders, Laka. It is also considered a symbol of love, beauty, and grace.
- Frangipani is popular in the art of tattooing, and the flowers and leaves are often used as motifs in traditional tattoos, particularly in Polynesia.
- Frangipani is toxic if ingested, it contains compounds called anthocyanins and alkaloids, which can cause skin irritation and stomach upset.
- Frangipani flowers are used in perfumery, the flowers are also used to extract essential oil which is used in perfumes, aromatherapy, and traditional medicine.
- Frangipani is also known for its medicinal properties, particularly the flowers and the sap. They are used to treat a variety of ailments, including fever, skin disorders and headaches.
Bringing Sentosa Home: The Perfect Way to Remember Your Island Getaway
In the Western Ghats of Karnataka, the bride and groom exchange garlands of cream-colored plumeria during weddings. Red colored flowers are not used in weddings. Plumeria plants are found in most of the temples in these regions.
Frangipani (Plumeria) holds a significant religious and cultural significance in many parts of the world, particularly in Asia and the Pacific islands. Here are a few examples of its religious significance:
Frangipani (Plumeria) holds a significant religious and cultural significance in many parts of the world, particularly in Asia and the Pacific islands. Here are a few examples of its religious significance:
- In Hinduism, Frangipani is associated with the god Vishnu and is considered a symbol of immortality and spiritual awakening. The flowers are often used in religious ceremonies and are often planted near temples.
- In Buddhism, Frangipani is associated with the bodhi tree, under which the Buddha attained enlightenment. The flowers are also used in traditional floral offerings to the Buddha.
- In Polynesian cultures, Frangipani is associated with the gods and goddesses and is often used in religious ceremonies and rituals. The flowers are also used to make lei, a traditional Hawaiian garland worn around the neck.
- In Laos, Frangipani is the national flower and is considered a symbol of good luck and prosperity. It is often planted near temples and other religious sites.
- In Hawaii, Frangipani is associated with the goddess of canoe builders, Laka, and is considered a symbol of love, beauty, and grace.
- In many cultures, Frangipani is associated with spiritual and mystical properties, it is often planted near temples and other religious sites, and is used in traditional floral arrangements and art.
- Frangipani flowers have a sweet and heady scent, which makes it a natural fit for religious and spiritual rituals. The scent is also associated with peace, purity, and spiritual transcendence.
Exploring the Botanical Wonders: The Flora Behind the Frangipani Scent
Frangipani (Plumeria) is known for its sweet, heady, and intoxicating scent. The scent is often described as a combination of fruity, floral, and slightly spicy notes. The fragrance is strongest at night when the flowers are in full bloom.
The scent of Frangipani is composed of several compounds, including:
Frangipani (Plumeria) is known for its sweet, heady, and intoxicating scent which comes from a combination of natural compounds and synthetic aromachemicals. Here are a few examples of aromachemicals that can be used to replicate the scent of Frangipani in perfumes and other fragranced products:
The scent of Frangipani is composed of several compounds, including:
- Monoterpenes such as linalool, which give the flower its floral and sweet aroma.
- Sesquiterpenes such as β-caryophyllene and α-humulene, which give the flower its spicy and woody notes.
- Phenylpropanoids such as eugenol, which give the flower its fruity and spicy aroma.
- Essential oil of Frangipani is used in perfumery, aromatherapy, and traditional medicine. The oil is extracted from the flowers and leaves and is known for its calming and relaxing properties.
- Frangipani's scent is also used in perfumes, candles, soaps, lotions, and other personal care products. The fragrance is considered to evoke feelings of serenity, relaxation, and spiritual transcendence.
- Frangipani's scent is also known for its strong association with tropical and exotic locations, which makes it a popular choice for perfumes and personal care products inspired by tropical destinations.
Frangipani (Plumeria) is known for its sweet, heady, and intoxicating scent which comes from a combination of natural compounds and synthetic aromachemicals. Here are a few examples of aromachemicals that can be used to replicate the scent of Frangipani in perfumes and other fragranced products:
- Linalool - This is a natural compound found in many plants, including Frangipani. It is used to replicate the floral and sweet aroma of the flower.
- Linalyl Acetate - This is another natural compound found in Frangipani. It is used to replicate the floral and sweet aroma of the flower.
- Beta-Caryophyllene - This is a natural compound found in many plants, including Frangipani. It is used to replicate the spicy and woody notes of the flower.
- Alpha-Humulene - This is a natural compound found in many plants, including Frangipani. It is used to replicate the spicy and woody notes of the flower.
- Eugenol - This is a natural compound found in many plants, including Frangipani. It is used to replicate the fruity and spicy aroma of the flower.
- Iso e Super - This is an synthetic aroma chemical that is used to replicate the sweet, woody and amber scent of the Frangipani
- Hedione - This is an synthetic aroma chemical that is used to replicate the fresh and floral scent of the Frangipani
Experience Sentosa through Fragrance: Frangipani Perfume Explained
Frangipani is a popular scent note in many perfumes, particularly those that are inspired by tropical and exotic locations. Here are a few examples of famous brand perfumes that feature Frangipani as a scent note:
- Tom Ford's "Tropical Rain" - Frangipani is one of the main scent notes in this perfume, which also features notes of coconut, ylang-ylang, and vanilla.
- Jo Malone's "Frangipani Flower" - This perfume is inspired by the Frangipani flower and features a heady and sweet scent that is true to the flower's natural fragrance.
- Le Labo's "Tiaré" - Frangipani is one of the main scent notes in this perfume, which also features notes of coconut, vanilla, and ylang-ylang.
- Byredo's "Tropical Sunset" - Frangipani is one of the main scent notes in this perfume, which also features notes of coconut, orange, and vanilla.
- Diptyque's "Tiaré" - Frangipani is one of the main scent notes in this perfume, which also features notes of ylang-ylang, coconut, and vanilla.
- L'Artisan Parfumeur's "Fleur de Carotte" - Frangipani is one of the main scent notes in this perfume, which also features notes of carrot, orange, and jasmine.
Join Scentopia, Sentosa's latest tourist attraction wonderful orchid scent crafting, fragrance tour, bridal shower or corporate team building which includes perfume making onsite and offsite, beach activities and more. We also serve primary school learning journey, secondary students and pupil on industrial excursions. Know more about our orchids perfume bar or therapeutic orchid scents and other wellness aromas. Conatct Perfume workshop or book a scent crafting session here.