Pomegranate: The Ruby-Red Gem of Fragrance, Flavor, and Potential Wellness
Introduction: Pomegranate, with its ruby-red allure and unique taste, is a cherished fruit celebrated for its delightful flavor, fragrance, and potential health benefits. Scientifically known as Punica granatum, this exotic fruit belongs to the Lythraceae family and has a rich history dating back thousands of years. From inspiring perfumers with its sweet and tangy aroma to offering potential benefits in therapeutic oils and traditional medicine, pomegranate is more than just a fruit. This essay delves into the captivating world of pomegranate, encompassing its presence in perfumes, therapeutic oils, food, medicinal systems, historical significance, and intriguing fun facts about this extraordinary and cherished fruit.
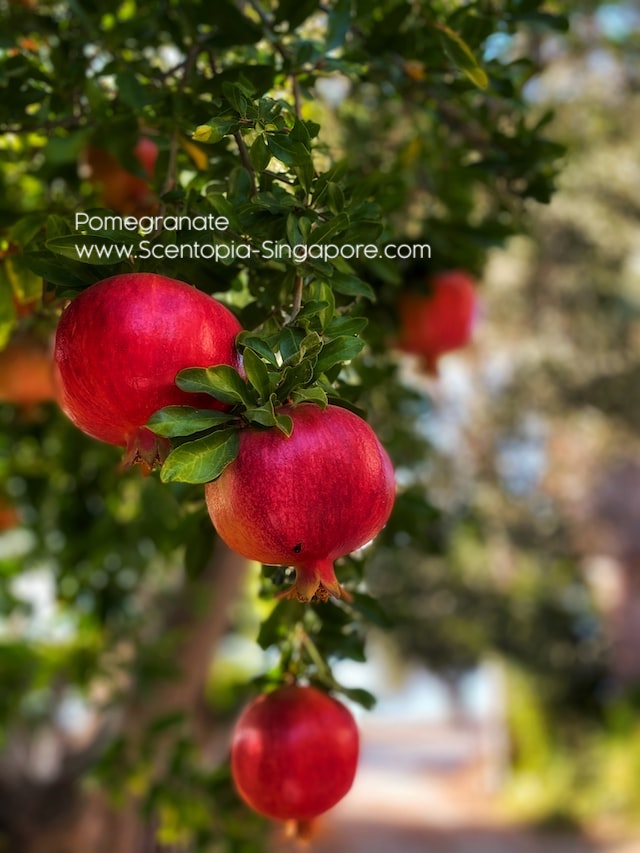
The Enchantment of Pomegranate: Pomegranate is renowned for its unique appearance, with its crown-like calyx and a multitude of jewel-like seeds (arils) encased in its leathery skin. Its sweet and tangy flavor, along with its potential health benefits, has made it a favorite fruit in culinary traditions around the world.
Perfumes and Fragrance: Pomegranate's sweet and tangy aroma has inspired perfumers to create alluring scents reminiscent of its fruity essence. Pomegranate-inspired perfumes often evoke feelings of freshness, vibrancy, and sensuality, making them popular choices for those seeking a touch of exotic allure.
Therapeutic Oils and Aromatherapy: Pomegranate essential oil is not commonly available, but certain therapeutic oils with fruity and uplifting characteristics, such as sweet orange or grapefruit essential oil, may be used in aromatherapy to promote a positive mood and reduce stress.
Medicinal Applications: Pomegranate has a long history of use in traditional medicine systems. The fruit and its juice are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making them valuable for supporting heart health, boosting immunity, and promoting overall well-being. Pomegranate extracts are also used in skincare products for their potential anti-aging and skin-rejuvenating properties.
Culinary Delights: Pomegranate is a versatile fruit used in various culinary creations. It is enjoyed fresh, juiced, or sprinkled as arils on salads, desserts, and savory dishes. Its vibrant color and sweet-tart flavor add a delightful touch to a wide range of recipes.
Historical Significance: Pomegranate has a deep-rooted history in various cultures and mythologies. It has been revered as a symbol of fertility, prosperity, and abundance in ancient civilizations. In Greek mythology, the pomegranate is associated with the story of Persephone and the changing seasons.
Fun and Crazy Facts:
Introduction: Pomegranate, with its ruby-red allure and unique taste, is a cherished fruit celebrated for its delightful flavor, fragrance, and potential health benefits. Scientifically known as Punica granatum, this exotic fruit belongs to the Lythraceae family and has a rich history dating back thousands of years. From inspiring perfumers with its sweet and tangy aroma to offering potential benefits in therapeutic oils and traditional medicine, pomegranate is more than just a fruit. This essay delves into the captivating world of pomegranate, encompassing its presence in perfumes, therapeutic oils, food, medicinal systems, historical significance, and intriguing fun facts about this extraordinary and cherished fruit.
The Enchantment of Pomegranate: Pomegranate is renowned for its unique appearance, with its crown-like calyx and a multitude of jewel-like seeds (arils) encased in its leathery skin. Its sweet and tangy flavor, along with its potential health benefits, has made it a favorite fruit in culinary traditions around the world.
Perfumes and Fragrance: Pomegranate's sweet and tangy aroma has inspired perfumers to create alluring scents reminiscent of its fruity essence. Pomegranate-inspired perfumes often evoke feelings of freshness, vibrancy, and sensuality, making them popular choices for those seeking a touch of exotic allure.
Therapeutic Oils and Aromatherapy: Pomegranate essential oil is not commonly available, but certain therapeutic oils with fruity and uplifting characteristics, such as sweet orange or grapefruit essential oil, may be used in aromatherapy to promote a positive mood and reduce stress.
Medicinal Applications: Pomegranate has a long history of use in traditional medicine systems. The fruit and its juice are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making them valuable for supporting heart health, boosting immunity, and promoting overall well-being. Pomegranate extracts are also used in skincare products for their potential anti-aging and skin-rejuvenating properties.
Culinary Delights: Pomegranate is a versatile fruit used in various culinary creations. It is enjoyed fresh, juiced, or sprinkled as arils on salads, desserts, and savory dishes. Its vibrant color and sweet-tart flavor add a delightful touch to a wide range of recipes.
Historical Significance: Pomegranate has a deep-rooted history in various cultures and mythologies. It has been revered as a symbol of fertility, prosperity, and abundance in ancient civilizations. In Greek mythology, the pomegranate is associated with the story of Persephone and the changing seasons.
Fun and Crazy Facts:
- Ancient Symbolism: Pomegranate is a symbol of fertility and abundance in many cultures. In ancient Greece, it was associated with the goddess Demeter and represented regeneration and renewal.
- Pomegranate in Art: Pomegranate motifs have been found in ancient art and architecture, dating back to thousands of years ago.
- Health Benefits: Pomegranate is rich in antioxidants, particularly punicalagins and anthocyanins, which are believed to help protect the body against free radicals and oxidative stress.
- Pomegranate Trees: Pomegranate trees are drought-resistant and can live for over 200 years, bearing fruit annually.
- Pomegranate in Ancient Egypt: Pomegranates were considered symbols of prosperity and were often placed in tombs to ensure a fruitful afterlife.
To experience augmented reality, please open the Facebook-app using QR code and point to the image below
Pomegranate is a fruit that grows on a small tree or shrub in the Lythraceae family. The fruit has a thick, leathery red or yellow-red skin and contains numerous seeds, called arils, that are surrounded by a sweet, tart, juicy flesh. Pomegranates are high in vitamins C and K, and antioxidants. They are commonly consumed fresh, juiced, or as a flavoring in food and drinks. The pomegranate is a symbol of many things in different cultures, including fertility, abundance, and eternal life.
Pomegranates have a long history of cultivation and use dating back to ancient civilizations. They were believed to have originated in the region of modern-day Iran and were cultivated in Mesopotamia and the eastern Mediterranean as early as 4000 BC. The ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all had a high regard for the fruit and it was often depicted in art and literature. In ancient Greece, it was a symbol of fertility and prosperity and was dedicated to the goddess Aphrodite. The pomegranate was also an important symbol in ancient Egypt and was associated with the goddess Isis.
Pomegranates spread throughout the Mediterranean and into Africa and Asia through trade and were eventually brought to the Americas by Spanish colonizers. Today, pomegranates are widely cultivated in many regions of the world, including the Middle East, Mediterranean, India, China, and California.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the health benefits of pomegranates and their juice, which is rich in antioxidants and has been linked to a number of health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and fighting cancer.
Pomegranates have a long history of cultivation and use dating back to ancient civilizations. They were believed to have originated in the region of modern-day Iran and were cultivated in Mesopotamia and the eastern Mediterranean as early as 4000 BC. The ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all had a high regard for the fruit and it was often depicted in art and literature. In ancient Greece, it was a symbol of fertility and prosperity and was dedicated to the goddess Aphrodite. The pomegranate was also an important symbol in ancient Egypt and was associated with the goddess Isis.
Pomegranates spread throughout the Mediterranean and into Africa and Asia through trade and were eventually brought to the Americas by Spanish colonizers. Today, pomegranates are widely cultivated in many regions of the world, including the Middle East, Mediterranean, India, China, and California.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the health benefits of pomegranates and their juice, which is rich in antioxidants and has been linked to a number of health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and fighting cancer.
Pomegranates have been used in many religious and cultural traditions throughout history.
In Jewish culture, the pomegranate is considered a symbol of righteousness and fruitfulness, and is featured prominently in Jewish art and literature. The Talmud states that the pomegranate contains 613 seeds, which corresponds to the 613 commandments in the Torah. As a result, the pomegranate is often used as a symbol of the Torah and Jewish learning.
In Christianity, the pomegranate is a symbol of the resurrection of Christ and the promise of eternal life. It is also associated with the Virgin Mary and is sometimes depicted in Christian art as a symbol of the Church.
In Islamic culture, the pomegranate is considered to be a symbol of abundance and is often used in art and architecture. The Prophet Muhammad is said to have said that eating pomegranates is good for the heart.
In Hinduism, the pomegranate is associated with the goddess Kali and is offered as a symbol of fertility and prosperity during religious ceremonies. In Buddhism, the pomegranate is associated with the bodhi tree and symbolizes the attainment of enlightenment.
In all of these cultures, the pomegranate is seen as a symbol of fertility, prosperity, and abundance and is associated with the afterlife and eternal life.
In Jewish culture, the pomegranate is considered a symbol of righteousness and fruitfulness, and is featured prominently in Jewish art and literature. The Talmud states that the pomegranate contains 613 seeds, which corresponds to the 613 commandments in the Torah. As a result, the pomegranate is often used as a symbol of the Torah and Jewish learning.
In Christianity, the pomegranate is a symbol of the resurrection of Christ and the promise of eternal life. It is also associated with the Virgin Mary and is sometimes depicted in Christian art as a symbol of the Church.
In Islamic culture, the pomegranate is considered to be a symbol of abundance and is often used in art and architecture. The Prophet Muhammad is said to have said that eating pomegranates is good for the heart.
In Hinduism, the pomegranate is associated with the goddess Kali and is offered as a symbol of fertility and prosperity during religious ceremonies. In Buddhism, the pomegranate is associated with the bodhi tree and symbolizes the attainment of enlightenment.
In all of these cultures, the pomegranate is seen as a symbol of fertility, prosperity, and abundance and is associated with the afterlife and eternal life.
Pomegranates are known to have a number of health benefits due to their high antioxidant content. Some of the key health benefits of pomegranates include:
- Heart health: Pomegranates contain high levels of antioxidants, particularly punicalagins and punicic acid, which have been shown to help lower blood pressure and improve blood flow to the heart.
- Anti-inflammatory: Pomegranates have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes.
- Cancer prevention: Pomegranates contain compounds that have been shown to have anti-cancer properties and may help prevent the growth and spread of cancer cells.
- Arthritis: Pomegranates have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
- Digestive health: Pomegranates contain high levels of fiber which can help promote regular bowel movements and improve overall digestive health.
- Brain health: Pomegranates contain antioxidants that can help improve cognitive function and protect the brain from damage.
Pomegranates are known to have a number of health benefits due to their high antioxidant content. Some of the key health benefits of pomegranates include:
- Heart health: Pomegranates contain high levels of antioxidants, particularly punicalagins and punicic acid, which have been shown to help lower blood pressure and improve blood flow to the heart.
- Anti-inflammatory: Pomegranates have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes.
- Cancer prevention: Pomegranates contain compounds that have been shown to have anti-cancer properties and may help prevent the growth and spread of cancer cells.
- Arthritis: Pomegranates have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
- Digestive health: Pomegranates contain high levels of fiber which can help promote regular bowel movements and improve overall digestive health.
- Brain health: Pomegranates contain antioxidants that can help improve cognitive function and protect the brain from damage.
A fun fact about pomegranates is that they were considered a symbol of prosperity and abundance in ancient times. According to Greek mythology, Persephone, the goddess of spring and wife of Hades, was kidnapped and taken to the underworld. Her mother Demeter, the goddess of the harvest, was so grief-stricken that she caused all of the crops to wither and die. To get Persephone back, Hades agreed to release her, but only if she ate nothing while in the underworld. Persephone, however, was tricked into eating six pomegranate seeds, which bound her to return to the underworld for six months every year, causing the earth to become barren during that time, a story that is believed to be the origin of the seasons.
The scent profile of pomegranates can vary depending on the variety and ripeness of the fruit. In general, pomegranates have a sweet and tangy aroma with notes of tartness and a hint of floral undertones. When the fruit is ripe, it will have a strong and sweet aroma. The rind of a pomegranate may have a slight bitter smell when it is green, but as it ripens the smell will become more sweet and fruity.
The juice of a pomegranate is also very aromatic, with a fruity and slightly tart smell. The juice may have a slight earthy smell as well, which can be attributed to the presence of tannins. When pomegranate is used in perfumes it can bring a fruity, sweet, and tangy scent profile, but also it can bring floral and spicy undertones that can come from the use of essential oils extracted from the rind or flowers of the pomegranate.
Pomegranate is considered a versatile ingredient in perfumery and it can be used to create a wide variety of scents, from sweet and fruity to floral and spicy. The scent profile of pomegranates is primarily due to the presence of several volatile compounds, including esters, alcohols, and terpenes.
Esters, such as ethyl butyrate and ethyl hexanoate, are responsible for the sweet and fruity aroma of pomegranates. Alcohols, such as 1-octen-3-ol, also contribute to the sweet and fruity aroma, as well as a floral undertone. Terpenes, such as limonene, contribute to the tangy and citrusy aroma of pomegranates. Limonene is also present in many other citrus fruits and is known for its refreshing and uplifting scent.
Other compounds that contribute to the scent profile of pomegranates include phenolic compounds, such as ellagic acid, and flavonoids, such as quercetin. These compounds contribute to the overall aroma and flavor of pomegranates, but also have health benefits. It's worth noting that the chemical composition of pomegranates can vary depending on the variety, growing conditions, and the stage of ripeness. Therefore, the scent profile of different pomegranates can vary.
The scent profile of pomegranates can vary depending on the variety and ripeness of the fruit. In general, pomegranates have a sweet and tangy aroma with notes of tartness and a hint of floral undertones. When the fruit is ripe, it will have a strong and sweet aroma. The rind of a pomegranate may have a slight bitter smell when it is green, but as it ripens the smell will become more sweet and fruity.
The juice of a pomegranate is also very aromatic, with a fruity and slightly tart smell. The juice may have a slight earthy smell as well, which can be attributed to the presence of tannins. When pomegranate is used in perfumes it can bring a fruity, sweet, and tangy scent profile, but also it can bring floral and spicy undertones that can come from the use of essential oils extracted from the rind or flowers of the pomegranate.
Pomegranate is considered a versatile ingredient in perfumery and it can be used to create a wide variety of scents, from sweet and fruity to floral and spicy. The scent profile of pomegranates is primarily due to the presence of several volatile compounds, including esters, alcohols, and terpenes.
Esters, such as ethyl butyrate and ethyl hexanoate, are responsible for the sweet and fruity aroma of pomegranates. Alcohols, such as 1-octen-3-ol, also contribute to the sweet and fruity aroma, as well as a floral undertone. Terpenes, such as limonene, contribute to the tangy and citrusy aroma of pomegranates. Limonene is also present in many other citrus fruits and is known for its refreshing and uplifting scent.
Other compounds that contribute to the scent profile of pomegranates include phenolic compounds, such as ellagic acid, and flavonoids, such as quercetin. These compounds contribute to the overall aroma and flavor of pomegranates, but also have health benefits. It's worth noting that the chemical composition of pomegranates can vary depending on the variety, growing conditions, and the stage of ripeness. Therefore, the scent profile of different pomegranates can vary.
Pomegranate is a popular note in many famous perfumes. Here are a few examples:
- Jo Malone Pomegranate Noir: This fragrance features a prominent pomegranate note, paired with spicy pink pepper, Casablanca lily, and patchouli.
- Yves Saint Laurent Black Opium: This perfume features a prominent pomegranate note, paired with notes of coffee, vanilla, and white flowers.
- Tom Ford Black Orchid: This fragrance features a prominent pomegranate note, paired with notes of black truffle, bergamot, and vanilla.
- Marc Jacobs Daisy Dream: This perfume features a prominent pomegranate note, paired with notes of blackberry, jasmine, and white woods.
- Gucci Bloom: This fragrance features a prominent pomegranate note, paired with notes of jasmine, tuberose, and Rangoon creeper.
Join Scentopia, Sentosa's latest tourist attraction wonderful orchid scent crafting, fragrance tour, bridal shower or corporate team building which includes perfume making onsite and offsite, beach activities and more. We also serve primary school learning journey, secondary students and pupil on industrial excursions. Know more about our orchids perfume bar or therapeutic orchid scents and other wellness aromas. Conatct Perfume workshop or book a scent crafting session here.