Embrace the Essence of Sun-Kissed Shores
Coconut: The Versatile Wonder of Nature
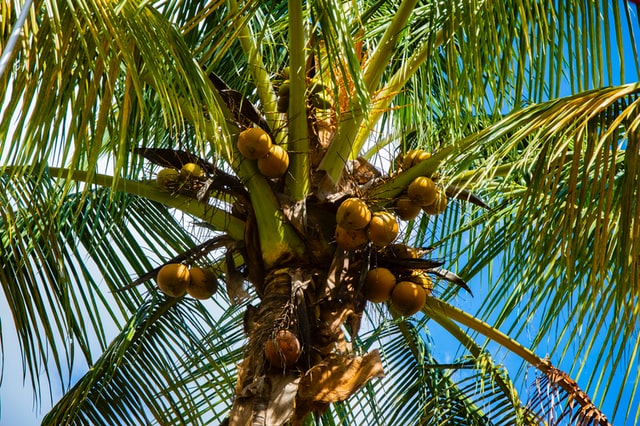
The coconut tree (Cocos nucifera) is often referred to as the "tree of life" due to its many practical uses and benefits. From perfumes and fragrance to therapeutic oils, food, medicinal systems, history, and fun crazy facts, the coconut holds a prominent place in the hearts and lives of people around the world.
Aromatic Elegance in Perfumes and Fragrances: The scent of coconut exudes a sense of tropical paradise and relaxation, making it a popular choice in perfumes and fragrances. Its warm and sweet aroma evokes memories of sandy beaches and palm trees swaying in the breeze. Coconut notes are often incorporated into summery and exotic fragrance blends, bringing a touch of the tropics to the wearer.
Therapeutic Properties in Coconut Oil: Coconut oil, extracted from the meat of the coconut, has gained popularity as a therapeutic oil with a myriad of health benefits. It is rich in medium-chain fatty acids, lauric acid, and antioxidants. Coconut oil is commonly used in aromatherapy massages for its moisturizing and skin-nourishing properties. Additionally, it is believed to promote relaxation and stress relief.
Nutrition and Culinary Delight: Coconut is a staple food in many tropical regions, and its culinary applications are vast. Coconut water, found inside young coconuts, is a natural electrolyte-rich beverage, often referred to as "nature's sports drink." Coconut milk, derived from grated coconut flesh, is a creamy and flavorful ingredient in various cuisines, especially in South Asian and Southeast Asian dishes. Coconut oil is a popular cooking oil, known for its high smoke point and distinct taste.
Medicinal Uses in Traditional Medicine: In traditional medicine systems, various parts of the coconut tree are used for their medicinal properties. Coconut water is believed to have hydrating and cooling effects on the body. Coconut oil is used in natural remedies for skincare, haircare, and digestive health. In some cultures, coconut husk fibers and coconut shell charcoal are used for wound dressing and poultices.
Historical Significance and Cultural Relevance: The coconut tree is believed to have originated in Southeast Asia and the Indian Ocean region. It has been a significant part of the culture and livelihood of people in these areas for centuries. In ancient times, coconuts were highly valued commodities and were traded across different regions.
Fun and Crazy Facts:
The coconut's versatility is awe-inspiring, as it encompasses a wide range of uses and applications across different industries and cultures. From the aromatic allure in perfumes and fragrances to the therapeutic properties of coconut oil, the nutritional value in culinary delights, and the historical significance in traditional medicine, the coconut is truly a wonder of nature. Its impact on human life, health, and well-being, along with its cultural significance and fascinating fun facts, make the coconut a beloved and cherished treasure that continues to enrich and nourish lives worldwide.
The coconut tree (Cocos nucifera) is often referred to as the "tree of life" due to its many practical uses and benefits. From perfumes and fragrance to therapeutic oils, food, medicinal systems, history, and fun crazy facts, the coconut holds a prominent place in the hearts and lives of people around the world.
Aromatic Elegance in Perfumes and Fragrances: The scent of coconut exudes a sense of tropical paradise and relaxation, making it a popular choice in perfumes and fragrances. Its warm and sweet aroma evokes memories of sandy beaches and palm trees swaying in the breeze. Coconut notes are often incorporated into summery and exotic fragrance blends, bringing a touch of the tropics to the wearer.
Therapeutic Properties in Coconut Oil: Coconut oil, extracted from the meat of the coconut, has gained popularity as a therapeutic oil with a myriad of health benefits. It is rich in medium-chain fatty acids, lauric acid, and antioxidants. Coconut oil is commonly used in aromatherapy massages for its moisturizing and skin-nourishing properties. Additionally, it is believed to promote relaxation and stress relief.
Nutrition and Culinary Delight: Coconut is a staple food in many tropical regions, and its culinary applications are vast. Coconut water, found inside young coconuts, is a natural electrolyte-rich beverage, often referred to as "nature's sports drink." Coconut milk, derived from grated coconut flesh, is a creamy and flavorful ingredient in various cuisines, especially in South Asian and Southeast Asian dishes. Coconut oil is a popular cooking oil, known for its high smoke point and distinct taste.
Medicinal Uses in Traditional Medicine: In traditional medicine systems, various parts of the coconut tree are used for their medicinal properties. Coconut water is believed to have hydrating and cooling effects on the body. Coconut oil is used in natural remedies for skincare, haircare, and digestive health. In some cultures, coconut husk fibers and coconut shell charcoal are used for wound dressing and poultices.
Historical Significance and Cultural Relevance: The coconut tree is believed to have originated in Southeast Asia and the Indian Ocean region. It has been a significant part of the culture and livelihood of people in these areas for centuries. In ancient times, coconuts were highly valued commodities and were traded across different regions.
Fun and Crazy Facts:
- Coconuts are considered to be "drupe" fruits, not nuts. They are botanically classified as a type of fruit.
- Coconut water is a natural isotonic beverage, and during World War II, it was used as an intravenous fluid in emergencies when regular saline was not available.
- The brown, hairy outer husk of the coconut is known as the "coir," and it is used to make ropes, mats, and brushes.
The coconut's versatility is awe-inspiring, as it encompasses a wide range of uses and applications across different industries and cultures. From the aromatic allure in perfumes and fragrances to the therapeutic properties of coconut oil, the nutritional value in culinary delights, and the historical significance in traditional medicine, the coconut is truly a wonder of nature. Its impact on human life, health, and well-being, along with its cultural significance and fascinating fun facts, make the coconut a beloved and cherished treasure that continues to enrich and nourish lives worldwide.
To experience augmented reality, please open the Facebook-app using QR code and point to the image below
Unisex Fragrance Inspired by Tropical Beaches
Coconut provides a high-calorie food, potable water, fiber that can be spun into rope, and a hard shell that can be turned into charcoal. In worst case scenario, it serves as a handy flotation device too. It is one of the most useful trees in the world and is often referred to as the "tree of life" in general. In India, it is called ‘Kalpavriksha’ a mythological tree supposed to grant all desires or – “the tree that provides all the necessities of life”. It is “Pokok seribu guna” (the tree of a thousand uses) to Malays, and “Tree of life” or “Tree of heaven” for a Filipino, “Tree of abundance” or “Three generations tree” to an Indonesian. The very names are reflective of its importance to people in the tropics.
The name coconut is derived from the 16th-century Portuguese and Spanish word coco, meaning 'head' or 'skull' after the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features. Coconut has a long history in Singapore, dating back to the time when the island was first settled. The coconut tree is well-suited to the tropical climate of Singapore and is able to grow in a variety of soils, making it an important crop for early settlers.
Coconuts were a valuable resource for the early inhabitants of Singapore, providing them with food, drink, and materials for shelter and tools. The coconut meat and milk were used as a source of food, while the coconut water was used as a refreshing drink. The husks and shells of the coconut were used to make items such as baskets, mats, and bowls. The trunk of the tree was used to make poles, and the leaves were used to make thatch for roofing.
During the colonial era in Singapore, coconut plantations were established by the British to produce copra (dried coconut meat) which was then used to extract oil. This led to a boom in the coconut industry and the opening of many coconut oil mills around the island. Today, coconuts are still an important crop in Singapore, but the focus is more on using the fruits for commercial and industrial purposes, such as for food, cosmetics, and biofuel. The coconut industry in Singapore also includes the production of coconut milk, coconut cream, and desiccated coconut for export.
In addition, it's worth mentioning that the coconut tree is a symbol of tropical island life and is often used in landscaping and tourism industry in Singapore. Sentosa is a popular island resort in Singapore known for its beaches, theme parks, and attractions. Coconuts are a common sight on Sentosa, as they are well-suited to the tropical climate of the island.
Coconuts can be found growing in various parts of Sentosa, including the beaches, where they provide shade for visitors. They are also often used in landscaping and can be seen in gardens and along walkways. Coconut juice and coconut desserts: Sentosa island is famous for its street food, and coconut-based snacks and desserts are popular. Visitors can enjoy coconut juice and various treats such as coconut ice cream, coconut pudding, and more.
Overall, coconuts are an important part of the island's tropical atmosphere and culture, and can be enjoyed in various ways during a visit to Sentosa.
The name coconut is derived from the 16th-century Portuguese and Spanish word coco, meaning 'head' or 'skull' after the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features. Coconut has a long history in Singapore, dating back to the time when the island was first settled. The coconut tree is well-suited to the tropical climate of Singapore and is able to grow in a variety of soils, making it an important crop for early settlers.
Coconuts were a valuable resource for the early inhabitants of Singapore, providing them with food, drink, and materials for shelter and tools. The coconut meat and milk were used as a source of food, while the coconut water was used as a refreshing drink. The husks and shells of the coconut were used to make items such as baskets, mats, and bowls. The trunk of the tree was used to make poles, and the leaves were used to make thatch for roofing.
During the colonial era in Singapore, coconut plantations were established by the British to produce copra (dried coconut meat) which was then used to extract oil. This led to a boom in the coconut industry and the opening of many coconut oil mills around the island. Today, coconuts are still an important crop in Singapore, but the focus is more on using the fruits for commercial and industrial purposes, such as for food, cosmetics, and biofuel. The coconut industry in Singapore also includes the production of coconut milk, coconut cream, and desiccated coconut for export.
In addition, it's worth mentioning that the coconut tree is a symbol of tropical island life and is often used in landscaping and tourism industry in Singapore. Sentosa is a popular island resort in Singapore known for its beaches, theme parks, and attractions. Coconuts are a common sight on Sentosa, as they are well-suited to the tropical climate of the island.
Coconuts can be found growing in various parts of Sentosa, including the beaches, where they provide shade for visitors. They are also often used in landscaping and can be seen in gardens and along walkways. Coconut juice and coconut desserts: Sentosa island is famous for its street food, and coconut-based snacks and desserts are popular. Visitors can enjoy coconut juice and various treats such as coconut ice cream, coconut pudding, and more.
Overall, coconuts are an important part of the island's tropical atmosphere and culture, and can be enjoyed in various ways during a visit to Sentosa.
Invigorating Coconut Aroma for Men and Women
The coconut has cultural and religious significance in certain societies, particularly in India, where it is used in Hindu rituals. It forms the basis of wedding and worship rituals in Hinduism, a coconut religion in Vietnam, and features in the origin myths of several societies. The falling nature of their mature fruit has led to preoccupation with death by coconut.
Here are some fun facts about coconuts:
Vasco de Gama’s & his sailors called “Coco”, a grimacing face or hobgoblin, hence they started to call the face-like fruit, "coco" too. The brown, hairy husk and three face-like dimples made them think the seed looked like a sort of spirit.
When the “coco” came to England, the suffix of nut was added and that’s how the name came about.
Here are some fun facts about coconuts:
- The coconut is known as the "tree of life" because it can provide food, water, and shelter.
- The coconut is not a nut, but a drupe, which means it's a fruit with a hard outer shell and a seed inside.
- Coconuts can float in water, which is why they are able to travel long distances and spread to new locations.
- A mature coconut tree can produce up to 75 fruits per year.
- The coconut tree can grow up to 98 feet tall, making it one of the tallest trees in the world.
- Coconuts are an excellent source of healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals, such as potassium, magnesium, and manganese.
- The coconut oil is used for many different purposes, including cooking, hair care, skin care, and as a biofuel.
- The coconut is a major crop in many tropical countries and is used in many traditional recipes, such as curry dishes and desserts.
- The fibers found in the husk of a coconut are used to make items such as rope, brushes, and mats.
- The leaves of the coconut tree can be used to make baskets, thatch for roofing, and other items.
- Falling coconuts kill 150 people every year – 10 times the number of people killed by sharks.
- May 8th is National Coconut Creme Pie Day.
- Coconut oil was the world’s leading vegetable oil until soybean oil took over in the 1960’s.
- There are more than 20 billion coconuts produced each year.
- During the Pacific War of 1941-45, coconut water was used to give emergency plasma transfusions to wounded soldiers.
Vasco de Gama’s & his sailors called “Coco”, a grimacing face or hobgoblin, hence they started to call the face-like fruit, "coco" too. The brown, hairy husk and three face-like dimples made them think the seed looked like a sort of spirit.
When the “coco” came to England, the suffix of nut was added and that’s how the name came about.
Experience the Allure of Fresh Beach Coconut Scent
Coconuts have been used by humans for thousands of years. The evolutionary origin of the coconut is under dispute, with theories stating that it may have evolved in Asia, South America, or on islands in the Pacific. Trees grow up to 30 m (98 ft) tall and can yield up to 30-75 fruits per year. Modern genetic studies have identified the center of origin of coconuts as being the region between Southwest Asia and Melanesia, where it shows greatest genetic diversity.
About 74% of the world's supply of coconuts derives from Indonesia, the Philippines, and India combined.
Coconuts have been used for medicinal purposes for centuries in traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine. Here are some ways in which coconuts are used therapeutically:
About 74% of the world's supply of coconuts derives from Indonesia, the Philippines, and India combined.
Coconuts have been used for medicinal purposes for centuries in traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine. Here are some ways in which coconuts are used therapeutically:
- Coconut oil is used as a natural moisturizer for the skin, and it is believed to help with skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis.
- Coconut oil is also used as a natural treatment for hair, as it is believed to help with hair growth, repair damage, and prevent hair breakage.
- Coconut water is a natural source of electrolytes and is often used as a sports drink to help with hydration and recovery after exercise.
- The lauric acid found in coconut oil is believed to have antimicrobial properties and may help to boost the immune system.
- In Ayurvedic medicine, coconut oil is used as a natural laxative and to help with digestion.
- Some studies suggest that consuming coconut oil may help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Coconut oil is also used as a carrier oil for aromatherapy, as it is believed to help enhance the effectiveness of essential oils.
Coconut benefits:
1- Highly nutritious- Coconuts are especially high in manganese, which is essential for bone health and the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and cholesterol. They’re also rich in copper and iron, which help form red blood cells, as well as selenium, an important antioxidant that protects your cells.
2- Heart health - Studies have found that people who live on Polynesian islands and frequently eat coconut meat have lower rates of heart disease than those who follow a Western diet
3- Blood sugar control- One rat study found that coconut had antidiabetic effects, possibly due to its arginine content. Arginine is an amino acid that’s important for the functioning of pancreatic cells, which release the hormone insulin to regulate your blood sugar level
4- Contains powerful antioxidants- Coconut meat contains phenolic compounds, which are antioxidants that may help protect cells from oxidative damage. The main phenolic compounds identified include- gallic acid, caffeic acid, salicylic acid, p-coumaric acid
1- Highly nutritious- Coconuts are especially high in manganese, which is essential for bone health and the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and cholesterol. They’re also rich in copper and iron, which help form red blood cells, as well as selenium, an important antioxidant that protects your cells.
2- Heart health - Studies have found that people who live on Polynesian islands and frequently eat coconut meat have lower rates of heart disease than those who follow a Western diet
3- Blood sugar control- One rat study found that coconut had antidiabetic effects, possibly due to its arginine content. Arginine is an amino acid that’s important for the functioning of pancreatic cells, which release the hormone insulin to regulate your blood sugar level
4- Contains powerful antioxidants- Coconut meat contains phenolic compounds, which are antioxidants that may help protect cells from oxidative damage. The main phenolic compounds identified include- gallic acid, caffeic acid, salicylic acid, p-coumaric acid
Elevate Your Fragrance Collection with Unisex Coconut Aroma
Coconut has a distinct, sweet and nutty aroma. The chemical compounds responsible for the aroma of coconut are mainly straight-chain and branched-chain fatty acids, esters, and alcohols. The main compounds found in the aroma of coconut are:
The aroma of coconut is also influenced by the method of processing, the type of coconut, and the maturity of the coconut. In general, fresh coconuts have a more intense and natural aroma, while the aroma of processed coconuts is more subdued.
- Caprylic acid (octanoic acid) : It's a medium-chain fatty acid that has a fruity and coconut-like aroma.
- Lauric acid (dodecanoic acid) : It's a long-chain fatty acid that has a creamy, soapy, and coconut-like aroma.
- Myristic acid (tetradecanoic acid) : It's a long-chain fatty acid that has a nutty, earthy, and coconut-like aroma.
- Caproic acid (hexanoic acid) : It's a medium-chain fatty acid that has a fruity and coconut-like aroma.
- Capric acid (decanoic acid) : It's a medium-chain fatty acid that has a fruity and coconut-like aroma.
- Esters such as ethyl ester of caprylic acid, ethyl ester of caproic acid and ethyl ester of lauric acid, they also contribute to the coconut aroma.
- Alcohols such as 2-hexanol, 2-octanol and 2-decanol are also present in the aroma of coconut.
The aroma of coconut is also influenced by the method of processing, the type of coconut, and the maturity of the coconut. In general, fresh coconuts have a more intense and natural aroma, while the aroma of processed coconuts is more subdued.
Crafted with Care for Your Olfactory Pleasure
Coconut is a popular note in many perfumes, particularly in tropical and beach-inspired fragrances. Here are a few examples of popular perfume brands that feature coconut as a prominent note:
- Tom Ford's "Coco Fraction" perfume, which combines coconut with notes of jasmine and vanilla.
- Estée Lauder's "Bronze Goddess" perfume, which features coconut as a prominent note, along with notes of amber and vanilla.
- Bobbi Brown's "Beach" perfume, which combines coconut with notes of sand jasmine and sea spray.
- Michael Kors' "Island" perfume, which features coconut as a prominent note, along with notes of hibiscus and tiare flower.
- Marc Jacobs' "Coconut Splash" perfume, which features coconut as a prominent note, along with notes of orange blossom and vanilla.
- Jo Malone's "Coconut Lime" perfume, which features coconut as a prominent note, along with notes of lime and ginger.
- Tom Daxon's "Coconut" perfume, which is a unisex scent that features coconut as a prominent note, along with notes of sandalwood and musk.
- Solinotes' "Coconut" perfume, which features a pure and natural coconut aroma.
Join Scentopia, Sentosa's latest tourist attraction wonderful orchid scent crafting, fragrance tour, bridal shower or corporate team building which includes perfume making onsite and offsite, beach activities and more. We also serve primary school learning journey, secondary students and pupil on industrial excursions. Know more about our orchids perfume bar or therapeutic orchid scents and other wellness aromas. Conatct Perfume workshop or book a scent crafting session here.