Capturing the Essence of Aquatic Floral Aromas
Water Hyacinth: The Aquatic Beauty with Diverse Uses and Intriguing Facts
Introduction: Water Hyacinth, with its striking beauty and versatile applications, is an aquatic plant celebrated for its presence in perfumes, therapeutic oils, and other practical uses. Scientifically known as Eichhornia crassipes, Water Hyacinth is a free-floating perennial plant native to South America but now found in various parts of the world. This aquatic beauty has both positive and negative associations, as it can be invasive in certain regions while also offering potential benefits in various industries. From inspiring perfumers with its delicate fragrance to its use in traditional medicine and innovative eco-friendly products, Water Hyacinth is more than just a floating plant. This essay delves into the captivating world of Water Hyacinth, encompassing its presence in perfumes, therapeutic oils, food, medicinal systems, historical significance, and intriguing fun facts about this extraordinary and versatile aquatic plant.
Water Hyacinth in Perfumes and Fragrance: While Water Hyacinth itself is not commonly used in perfumes, its delicate floral fragrance may serve as an inspiration for perfumers in creating scents that evoke a sense of nature and aquatic beauty.
Therapeutic Oils and Traditional Medicine: Water Hyacinth is not a common source of therapeutic oils in modern practices. However, in traditional medicine systems in certain regions, it may have been used for specific medicinal purposes.
Food and Culinary Uses: Water Hyacinth is not typically consumed as food due to its invasive nature and potential toxic properties. In some cultures, the seeds and young leaves have been used in traditional dishes, but caution is required due to the potential for toxicity.
Medicinal Uses and Historical Significance: In some traditional medicine systems, Water Hyacinth has been used to treat certain health conditions. However, its use in modern medicine is limited, and its potential for toxicity must be considered.
Invasive Species and Environmental Impact: Water Hyacinth is considered one of the world's most invasive aquatic plants. It can grow rapidly and cover large water bodies, negatively impacting ecosystems, water quality, and biodiversity.
Sustainable Uses and Eco-Friendly Products: Efforts are being made to turn the invasive Water Hyacinth into a sustainable resource. It has been used to make eco-friendly products like baskets, mats, and handicrafts, providing livelihood opportunities for communities affected by its invasive growth.
Fun and Crazy Facts:
Water Hyacinth, with its striking beauty and diverse uses, is an aquatic plant that has both fascinated and challenged humanity. From its potential inspiration in perfumery to its impact on ecosystems and innovative eco-friendly products, Water Hyacinth showcases the complexity of the natural world and the ingenuity of human efforts to harness its potential sustainably. As we explore the captivating world of Water Hyacinth and its intriguing fun facts, we are reminded of the need for responsible environmental management and the importance of finding a balance between appreciating the beauty of nature and addressing the challenges posed by invasive species.
Introduction: Water Hyacinth, with its striking beauty and versatile applications, is an aquatic plant celebrated for its presence in perfumes, therapeutic oils, and other practical uses. Scientifically known as Eichhornia crassipes, Water Hyacinth is a free-floating perennial plant native to South America but now found in various parts of the world. This aquatic beauty has both positive and negative associations, as it can be invasive in certain regions while also offering potential benefits in various industries. From inspiring perfumers with its delicate fragrance to its use in traditional medicine and innovative eco-friendly products, Water Hyacinth is more than just a floating plant. This essay delves into the captivating world of Water Hyacinth, encompassing its presence in perfumes, therapeutic oils, food, medicinal systems, historical significance, and intriguing fun facts about this extraordinary and versatile aquatic plant.
Water Hyacinth in Perfumes and Fragrance: While Water Hyacinth itself is not commonly used in perfumes, its delicate floral fragrance may serve as an inspiration for perfumers in creating scents that evoke a sense of nature and aquatic beauty.
Therapeutic Oils and Traditional Medicine: Water Hyacinth is not a common source of therapeutic oils in modern practices. However, in traditional medicine systems in certain regions, it may have been used for specific medicinal purposes.
Food and Culinary Uses: Water Hyacinth is not typically consumed as food due to its invasive nature and potential toxic properties. In some cultures, the seeds and young leaves have been used in traditional dishes, but caution is required due to the potential for toxicity.
Medicinal Uses and Historical Significance: In some traditional medicine systems, Water Hyacinth has been used to treat certain health conditions. However, its use in modern medicine is limited, and its potential for toxicity must be considered.
Invasive Species and Environmental Impact: Water Hyacinth is considered one of the world's most invasive aquatic plants. It can grow rapidly and cover large water bodies, negatively impacting ecosystems, water quality, and biodiversity.
Sustainable Uses and Eco-Friendly Products: Efforts are being made to turn the invasive Water Hyacinth into a sustainable resource. It has been used to make eco-friendly products like baskets, mats, and handicrafts, providing livelihood opportunities for communities affected by its invasive growth.
Fun and Crazy Facts:
- Rapid Growth: Water Hyacinth is known for its rapid growth rate. In favorable conditions, it can double its population in just a few days.
- Floating Abilities: Water Hyacinth has specialized air-filled sacs in its leaves and stems, allowing it to float on the water's surface.
- Phytoremediation: Despite its invasive nature, Water Hyacinth has been used for phytoremediation purposes, as it can absorb and remove pollutants from contaminated water bodies.
- Thomas Edison's Interest: In the early 20th century, Thomas Edison explored the potential of Water Hyacinth as a source of rubber. While the project was not successful, it showcases the plant's versatility.
- Musical Instruments: In some cultures, Water Hyacinth stems have been used to make musical instruments, such as reed flutes.
Water Hyacinth, with its striking beauty and diverse uses, is an aquatic plant that has both fascinated and challenged humanity. From its potential inspiration in perfumery to its impact on ecosystems and innovative eco-friendly products, Water Hyacinth showcases the complexity of the natural world and the ingenuity of human efforts to harness its potential sustainably. As we explore the captivating world of Water Hyacinth and its intriguing fun facts, we are reminded of the need for responsible environmental management and the importance of finding a balance between appreciating the beauty of nature and addressing the challenges posed by invasive species.
To experience augmented reality, please open the Facebook-app using QR code and point to the image below
Discover the Fragrance of Water Hyacinth
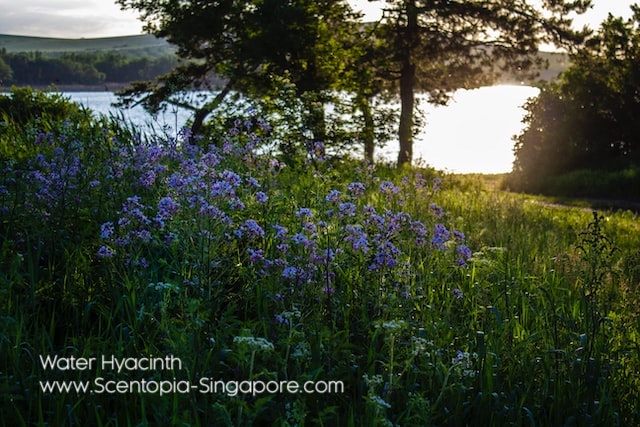
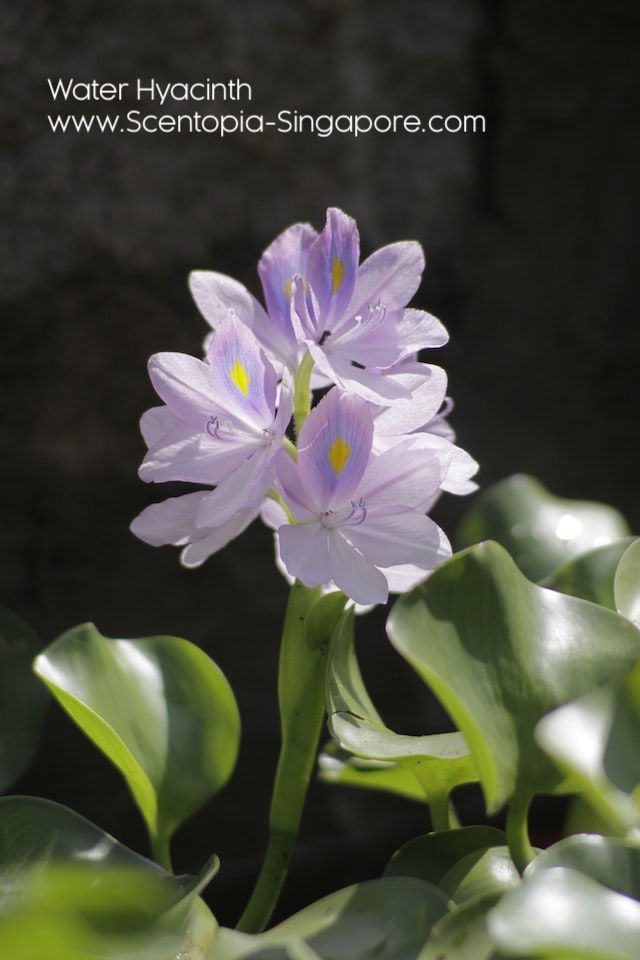
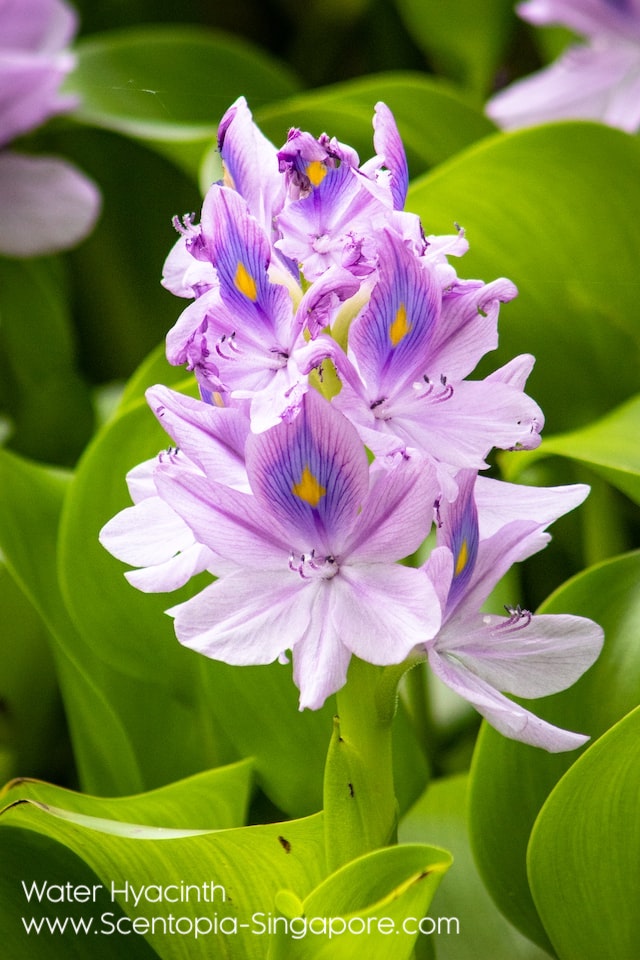
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is an aquatic plant native to South America that has become an invasive species in many parts of the world. It is a floating plant that has long, slender leaves and showy, fragrant flowers that are typically blue or purple.
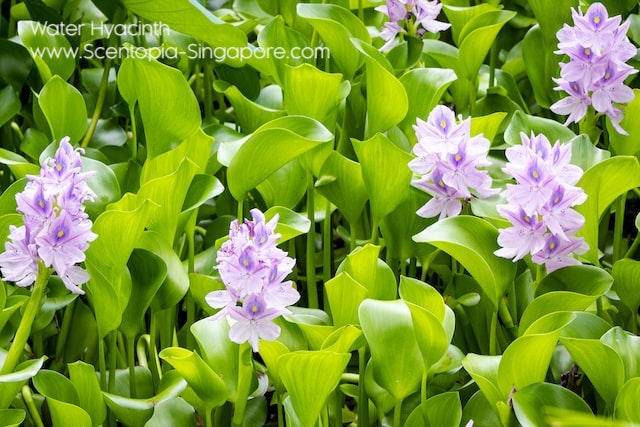
The plant is fast-growing and can form dense mats on the surface of rivers, lakes, and ponds, which can impact the ecology of these waterways by altering water quality, reducing oxygen levels, and displacing native aquatic species. It is considered an invasive species in many parts of the world, including Asia, Africa, and the United States, where it has been introduced and has spread beyond its native range.
Despite its negative impact on the environment, water hyacinth has been used for a variety of purposes, including erosion control, as a source of fuel and food, and as a natural biofilter for water treatment. In some regions, it is also used for weaving baskets, mats, and other products.
The plant is fast-growing and can form dense mats on the surface of rivers, lakes, and ponds, which can impact the ecology of these waterways by altering water quality, reducing oxygen levels, and displacing native aquatic species. It is considered an invasive species in many parts of the world, including Asia, Africa, and the United States, where it has been introduced and has spread beyond its native range.
Despite its negative impact on the environment, water hyacinth has been used for a variety of purposes, including erosion control, as a source of fuel and food, and as a natural biofilter for water treatment. In some regions, it is also used for weaving baskets, mats, and other products.
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is native to South America and has a long history of use in the region for various purposes, including as an ornamental plant and for medicine. The plant was introduced to other parts of the world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as an ornamental plant for water gardens and aquariums.
The plant quickly became invasive in many regions and spread rapidly beyond its original range. In some countries, it has caused significant ecological and economic harm by clogging waterways and impacting water quality, reducing fishing yields, and altering habitats for native species.
In response to its invasive status, various control measures have been developed and implemented, including biological control, chemical control, and mechanical removal. Despite these efforts, water hyacinth remains a major problem in many parts of the world, and ongoing management efforts are needed to address its impacts.
The plant quickly became invasive in many regions and spread rapidly beyond its original range. In some countries, it has caused significant ecological and economic harm by clogging waterways and impacting water quality, reducing fishing yields, and altering habitats for native species.
In response to its invasive status, various control measures have been developed and implemented, including biological control, chemical control, and mechanical removal. Despite these efforts, water hyacinth remains a major problem in many parts of the world, and ongoing management efforts are needed to address its impacts.
Fun Facts about Water Hyacinth
Here are some fun facts about water hyacinth:
- Water hyacinth is a very fast-growing plant and can double its size in just a few days.
- The plant's leaves are thick and spongy and can support the weight of a small child.
- Water hyacinth is considered a bio-accumulator, meaning it can absorb and concentrate heavy metals and other pollutants from the water.
- The plant's showy, fragrant flowers are a popular source of food for many species of bees and other pollinators.
- Water hyacinth has been used for a variety of purposes, including as a source of food and fuel, as a natural biofilter for water treatment, and as a natural material for weaving baskets and mats.
- In some cultures, the plant is used in traditional medicine for treating a variety of ailments, including headaches, fevers, and skin infections.
- Water hyacinth has a distinctive, light, and fresh scent that is often described as reminiscent of green apples or cucumbers.
Unveiling the Aquatic Notes of Our Perfume Collection
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is considered an invasive species in Singapore and is listed as one of the top 100 invasive species in the country. The plant was introduced to Singapore as an ornamental plant for water gardens and quickly became established in local waterways.
Water hyacinth can form dense mats on the surface of waterways, which can impact the ecology of these areas by altering water quality, reducing oxygen levels, and displacing native aquatic species. In addition, it can clog waterways, which can have economic impacts, such as reduced fishing yields and increased costs for water management and maintenance.
In response to its invasive status, the government of Singapore has taken a number of measures to control and manage the spread of water hyacinth, including monitoring and removing the plant from waterways, and raising public awareness about the dangers of introducing invasive species. Despite these efforts, water hyacinth remains a challenge in the country and ongoing management efforts are needed to address its impacts.
Water hyacinth can form dense mats on the surface of waterways, which can impact the ecology of these areas by altering water quality, reducing oxygen levels, and displacing native aquatic species. In addition, it can clog waterways, which can have economic impacts, such as reduced fishing yields and increased costs for water management and maintenance.
In response to its invasive status, the government of Singapore has taken a number of measures to control and manage the spread of water hyacinth, including monitoring and removing the plant from waterways, and raising public awareness about the dangers of introducing invasive species. Despite these efforts, water hyacinth remains a challenge in the country and ongoing management efforts are needed to address its impacts.
Experience Natural Elegance with Feminine Scents
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) has a distinctive, light, and fresh scent that is often described as reminiscent of green apples or cucumbers. The scent is most noticeable when the plant is in bloom and the flowers are open. The fragrance is produced by volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that are released from the flowers into the air. The scent of water hyacinth is not commonly used in perfumes or fragrances, but some people enjoy the fresh, green aroma and use it in potpourri or other fragrant products.
These VOCs include:
These VOCs include:
- Terpenoids such as limonene and terpinene
- Aldehydes such as hexanal and octanal
- Alcohols such as 1-hexanol and 2-hexanol
- Ketones such as acetone and 2-nonanone
- Esters such as ethyl hexanoate and ethyl nonanoate
While the plant does have a distinctive fresh and green scent, it is not commonly used as a fragrance ingredient in perfumes. Instead, more commonly used fragrance ingredients in perfumes include flowers such as roses, jasmine, and lavender, as well as woody and spicy notes like sandalwood, patchouli, and cinnamon.
Join Scentopia, Sentosa's latest tourist attraction wonderful orchid scent crafting, fragrance tour, bridal shower or corporate team building which includes perfume making onsite and offsite, beach activities and more. We also serve primary school learning journey, secondary students and pupil on industrial excursions. Know more about our orchids perfume bar or therapeutic orchid scents and other wellness aromas. Conatct Perfume workshop or book a scent crafting session here.