Coriander Green: Unveiling a Fresh and Revitalizing Perfume Note
Coriander: An Aromatic Herb with a Rich and Diverse Legacy!
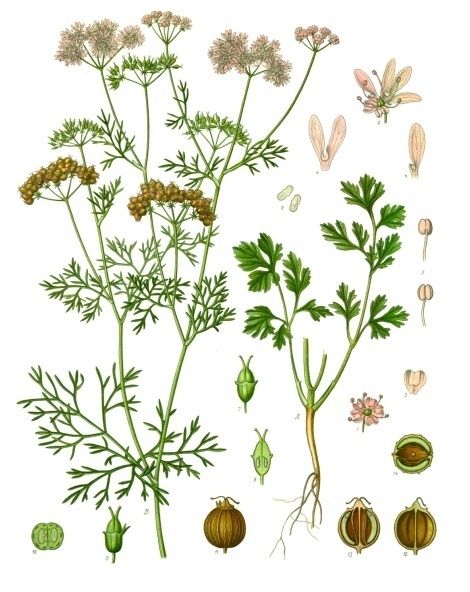
Coriander, also known as cilantro or Chinese parsley, is an aromatic herb that has been cultivated and cherished for its culinary, medicinal, and fragrant properties for thousands of years. This versatile herb is a member of the Apiaceae family and is native to regions in Southern Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia. Today, coriander is grown and enjoyed all over the world, playing a significant role in various cuisines and traditional medicine systems.
Historical Significance: Coriander has a storied history that dates back to ancient civilizations. It is one of the oldest known herbs, with evidence of its use dating as far back as 5,000 BCE in ancient Egypt. The ancient Egyptians used coriander in their culinary practices, and it was also found in the tombs of pharaohs as an offering to the gods.
Coriander's use spread to other parts of the world, including ancient Greece and Rome, where it was used as a spice and medicine. The ancient Greeks used coriander seeds as a spice, and it was mentioned in writings by Hippocrates, often referred to as the "father of medicine," for its medicinal properties.
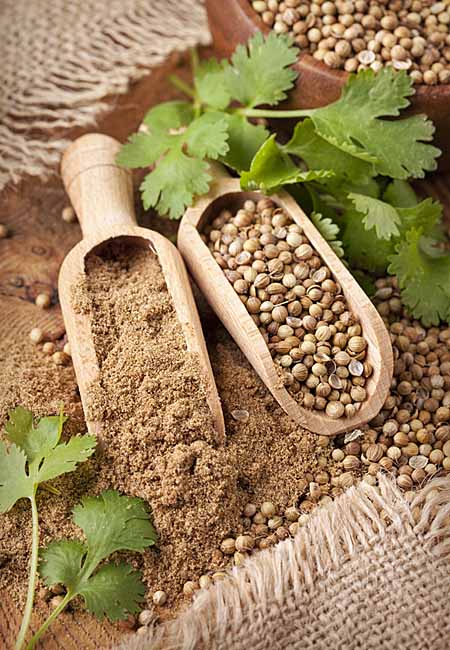
Culinary Use: Coriander is renowned for its distinctive flavor profile, which is citrusy, slightly sweet, and aromatic. Both the fresh leaves (cilantro) and the dried seeds are used in various culinary applications. In cuisines around the world, coriander is used in curries, soups, stews, salads, salsas, chutneys, and marinades. It is particularly popular in Indian, Mexican, Thai, and Middle Eastern cuisines, adding depth and complexity to dishes.
Fragrance and Perfumery: Coriander's fresh and citrusy scent has also made it a sought-after ingredient in perfumery. The essential oil obtained from coriander seeds has a bright and aromatic fragrance that blends well with other essential oils. It is often used as a middle note in perfumes to add a touch of freshness and depth.
Medicinal Benefits: In traditional medicine systems, coriander has been utilized for its various medicinal properties. Some of its potential health benefits include:
Therapeutic Oils and Aromatherapy: Coriander essential oil is used in aromatherapy for its soothing and relaxing properties. It is often incorporated into massage oils and diffuser blends to promote relaxation and calmness.
Modern Applications: In the modern world, coriander continues to be a beloved herb used in a wide range of culinary delights. It is also found in a variety of products such as herbal teas, herbal supplements, and cosmetic formulations.
Coriander's diverse legacy as a culinary delight, fragrant herb, and medicinal treasure spans centuries and cultures. From ancient Egypt to contemporary kitchens, its versatility and aromatic charm have made it a cherished ingredient in various applications. As we continue to explore its culinary, aromatic, and therapeutic potential, coriander remains a vibrant and beloved herb that delights the senses and enriches our lives.
Coriander, also known as cilantro or Chinese parsley, is an aromatic herb that has been cultivated and cherished for its culinary, medicinal, and fragrant properties for thousands of years. This versatile herb is a member of the Apiaceae family and is native to regions in Southern Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia. Today, coriander is grown and enjoyed all over the world, playing a significant role in various cuisines and traditional medicine systems.
Historical Significance: Coriander has a storied history that dates back to ancient civilizations. It is one of the oldest known herbs, with evidence of its use dating as far back as 5,000 BCE in ancient Egypt. The ancient Egyptians used coriander in their culinary practices, and it was also found in the tombs of pharaohs as an offering to the gods.
Coriander's use spread to other parts of the world, including ancient Greece and Rome, where it was used as a spice and medicine. The ancient Greeks used coriander seeds as a spice, and it was mentioned in writings by Hippocrates, often referred to as the "father of medicine," for its medicinal properties.
Culinary Use: Coriander is renowned for its distinctive flavor profile, which is citrusy, slightly sweet, and aromatic. Both the fresh leaves (cilantro) and the dried seeds are used in various culinary applications. In cuisines around the world, coriander is used in curries, soups, stews, salads, salsas, chutneys, and marinades. It is particularly popular in Indian, Mexican, Thai, and Middle Eastern cuisines, adding depth and complexity to dishes.
Fragrance and Perfumery: Coriander's fresh and citrusy scent has also made it a sought-after ingredient in perfumery. The essential oil obtained from coriander seeds has a bright and aromatic fragrance that blends well with other essential oils. It is often used as a middle note in perfumes to add a touch of freshness and depth.
Medicinal Benefits: In traditional medicine systems, coriander has been utilized for its various medicinal properties. Some of its potential health benefits include:
- Digestive Aid: Coriander is believed to aid digestion and help alleviate digestive discomfort.
- Anti-Inflammatory: The herb may possess anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for reducing inflammation in the body.
- Antioxidant: Coriander is rich in antioxidants, which help neutralize free radicals and protect cells from damage.
- Cholesterol Management: Some studies suggest that coriander may have a positive effect on cholesterol levels.
- Diabetes Management: Coriander may aid in managing blood sugar levels.
Therapeutic Oils and Aromatherapy: Coriander essential oil is used in aromatherapy for its soothing and relaxing properties. It is often incorporated into massage oils and diffuser blends to promote relaxation and calmness.
Modern Applications: In the modern world, coriander continues to be a beloved herb used in a wide range of culinary delights. It is also found in a variety of products such as herbal teas, herbal supplements, and cosmetic formulations.
Coriander's diverse legacy as a culinary delight, fragrant herb, and medicinal treasure spans centuries and cultures. From ancient Egypt to contemporary kitchens, its versatility and aromatic charm have made it a cherished ingredient in various applications. As we continue to explore its culinary, aromatic, and therapeutic potential, coriander remains a vibrant and beloved herb that delights the senses and enriches our lives.
To experience augmented reality, please open the Facebook-app using QR code and point to the image below
The Essence of Coriander Green Perfume Note
Coriander is one of the oldest herbs and spices on record. Coriander was mentioned in the Bible, and the seeds have been found in ruins dating back to 5000 B.C. Its name comes from the Greek word koris, meaning a stink bug.
3/4 people perceive the taste of coriander leaves as a likeable tart, lemon/lime taste, but to nearly 1/4, the leaves taste like dish soap. This is linked to a gene which detects some aldehydes. Hence, the love and hate relationship with coriander!
All parts of the plant are edible, but the fresh leaves and the dried seeds (as a spice) are the parts most traditionally used in cooking. The leaves spoil quickly when removed from the plant, and lose their aroma when dried or frozen.
Coriander (also known as cilantro) is a herb that is commonly used in cooking, particularly in Asian and Latin American cuisine. Sir Stamford Raffles, who is also known as Sir Thomas Stamford Bingley Raffles, was a British statesman, administrator, and founder of Singapore. In 1819, he established a British colony in Singapore, and played a major role in the development of Singapore as a major trading port in Southeast Asia. It is likely that coriander was present in Singapore during the time of Sir Raffles, as it is a popular herb in Southeast Asian cuisine. However, I couldn't find any specific reference of it in relation with him.
3/4 people perceive the taste of coriander leaves as a likeable tart, lemon/lime taste, but to nearly 1/4, the leaves taste like dish soap. This is linked to a gene which detects some aldehydes. Hence, the love and hate relationship with coriander!
All parts of the plant are edible, but the fresh leaves and the dried seeds (as a spice) are the parts most traditionally used in cooking. The leaves spoil quickly when removed from the plant, and lose their aroma when dried or frozen.
Coriander (also known as cilantro) is a herb that is commonly used in cooking, particularly in Asian and Latin American cuisine. Sir Stamford Raffles, who is also known as Sir Thomas Stamford Bingley Raffles, was a British statesman, administrator, and founder of Singapore. In 1819, he established a British colony in Singapore, and played a major role in the development of Singapore as a major trading port in Southeast Asia. It is likely that coriander was present in Singapore during the time of Sir Raffles, as it is a popular herb in Southeast Asian cuisine. However, I couldn't find any specific reference of it in relation with him.
Captivating Fresh Fragrance Ingredients
Coriander grows wild over a wide area of Western Asia and Southern Europe, prompting the comment: "It is hard to define exactly where this plant is wild and where it only recently established itself.
15 desiccated mericarps were found in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic cave (Nahal Hemar Cave) in Israel, which may be the oldest archaeological find of coriander.
About 500ml of coriander mericarps was found in the tomb of Tutankhamen. Since, the plant does not grow wild in Egypt, Zohary and Hopf interpret that coriander was cultivated by the ancient Egyptians. The Ebers Papyrus, an Egyptian medical text dated to around 1550 BC, describes coriander's medicinal and culinary uses.
In Greece, coriander has been cultivated since at least the second millennium BC. One of the Linear B tablets recovered from Pylos refers to the species as being cultivated for the manufacture of perfumes.
Large quantities of coriander retrieved from an Early Bronze Age layer at Sitagroi in Macedonia could point to cultivation of the species at that time. Later, coriander was mentioned by Hippocrates (c. 400 BC), as well as Dioscorides (65 AD).
Coriander (Coriandrum sativum) is a herb that is commonly used in cooking, and is also used in traditional medicine for a variety of ailments. The seeds and leaves of the plant are used in traditional medicine. Some of the traditional therapeutic uses of coriander include:
15 desiccated mericarps were found in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic cave (Nahal Hemar Cave) in Israel, which may be the oldest archaeological find of coriander.
About 500ml of coriander mericarps was found in the tomb of Tutankhamen. Since, the plant does not grow wild in Egypt, Zohary and Hopf interpret that coriander was cultivated by the ancient Egyptians. The Ebers Papyrus, an Egyptian medical text dated to around 1550 BC, describes coriander's medicinal and culinary uses.
In Greece, coriander has been cultivated since at least the second millennium BC. One of the Linear B tablets recovered from Pylos refers to the species as being cultivated for the manufacture of perfumes.
Large quantities of coriander retrieved from an Early Bronze Age layer at Sitagroi in Macedonia could point to cultivation of the species at that time. Later, coriander was mentioned by Hippocrates (c. 400 BC), as well as Dioscorides (65 AD).
Coriander (Coriandrum sativum) is a herb that is commonly used in cooking, and is also used in traditional medicine for a variety of ailments. The seeds and leaves of the plant are used in traditional medicine. Some of the traditional therapeutic uses of coriander include:
- Digestive aid: Coriander is believed to help with digestion and may be used to relieve stomach aches, gas, and bloating.
- Anti-inflammatory: Coriander has anti-inflammatory properties and may be used to reduce inflammation and swelling in conditions such as arthritis and eczema.
- Anti-anxiety: Coriander seeds are often used in traditional medicine as a natural remedy for anxiety and insomnia.
- Antimicrobial: Coriander has antimicrobial properties and has been traditionally used to treat infections such as candida and colitis.
- Blood sugar control: Coriander is believed to be beneficial for blood sugar control, research studies have found that coriander seed powder can reduce blood sugar levels in people with diabetes
Crafting Your Signature Perfume with Coriander Green
The dry fruits are coriander seeds. The seeds have a lemony citrus flavour when crushed, due to terpenes linalool and pinene. It is described as warm, nutty, spicy, and orange-flavoured. Although seeds generally have lower vitamin content, they do provide significant amounts of dietary fiber, calcium, selenium, iron, magnesium and manganese.
The essential oil from coriander leaves and seeds contains mixed polyphenols and terpenes, including linalool as the major constituent accounting for the aroma and flavor of coriander.
Coriander (Coriandrum sativum) has a distinct aroma that is characteristic of the plant. The aroma of coriander can be described as fresh, green, and slightly citrusy. The essential oil of coriander is obtained by steam distillation of the dried seeds and it is composed mainly of:
The essential oil from coriander leaves and seeds contains mixed polyphenols and terpenes, including linalool as the major constituent accounting for the aroma and flavor of coriander.
Coriander (Coriandrum sativum) has a distinct aroma that is characteristic of the plant. The aroma of coriander can be described as fresh, green, and slightly citrusy. The essential oil of coriander is obtained by steam distillation of the dried seeds and it is composed mainly of:
- Linalool: a terpene alcohol that is known for its floral and spicy aroma. It is present at high levels in the essential oil of coriander, and is responsible for much of the plant's characteristic aroma.
- Pinene: a terpene that imparts a fresh, woody aroma to the essential oil of coriander.
- Geraniol: an alcohol that has a floral, rose-like aroma.
- Limonene: a terpene that imparts a fresh, citrusy aroma to the essential oil of coriander.
- Cineole: also known as eucalyptol, it gives a fresh, woody and medicinal character to the essential oil.
A Symphony of Fresh and Herbal Notes
Asian cuisine is infused with herbs, most of which are found to be beneficial for the body. We found some benefits for coriander as well:
1- May help lower blood sugar - A study in rats with obesity and high blood sugar found that a single dose (9.1 mg per pound of body weight or 20 mg per kg) of coriander seed extract decreased blood sugar by 4 mmol/L in 6 hours, similar to the effects of the blood sugar medication glibenclamide
2- Rich in immune-boosting antioxidants- Coriander offers several antioxidants, which prevent cellular damage caused by free radicals. These compounds include terpinene, quercetin, and tocopherols, which may have anticancer, immune-boosting, and neuroprotective effects, according to test-tube and animal studies.
3- May benefit heart health- Coriander extract appears to act as a diuretic, helping your body flush excess sodium and water. This may lower your blood pressure.
4- May protect brain health- Animal studies demonstrate that coriander extract is nearly as effective as Diazepam, a common anxiety medication, at reducing symptoms of this condition.
5- May fight infections- Dodecenal, a compound in coriander, may fight bacteria like Salmonella, which can cause life-threatening food poisoning and affect 1.2 million people annually in the United States.
Please note that most of these are animal studies. More research is needed with regards to its efficacy in humans.
Coriander is a versatile and popular herb with a wide range of uses in perfumery, it brings freshness, woody and spicy character to perfumes. Its essential oil is used in perfumes to add complexity and depth to the scent. Some perfumeries might use coriander essential oil in their perfumes, however, it is not always listed as an ingredient on the packaging or advertising. Brands like Jo Malone, Le Labo, Byredo, Diptyque, and other niche or artisanal perfumers might use coriander in their perfumes, but it is always better to check with the brands themselves.
1- May help lower blood sugar - A study in rats with obesity and high blood sugar found that a single dose (9.1 mg per pound of body weight or 20 mg per kg) of coriander seed extract decreased blood sugar by 4 mmol/L in 6 hours, similar to the effects of the blood sugar medication glibenclamide
2- Rich in immune-boosting antioxidants- Coriander offers several antioxidants, which prevent cellular damage caused by free radicals. These compounds include terpinene, quercetin, and tocopherols, which may have anticancer, immune-boosting, and neuroprotective effects, according to test-tube and animal studies.
3- May benefit heart health- Coriander extract appears to act as a diuretic, helping your body flush excess sodium and water. This may lower your blood pressure.
4- May protect brain health- Animal studies demonstrate that coriander extract is nearly as effective as Diazepam, a common anxiety medication, at reducing symptoms of this condition.
5- May fight infections- Dodecenal, a compound in coriander, may fight bacteria like Salmonella, which can cause life-threatening food poisoning and affect 1.2 million people annually in the United States.
Please note that most of these are animal studies. More research is needed with regards to its efficacy in humans.
Coriander is a versatile and popular herb with a wide range of uses in perfumery, it brings freshness, woody and spicy character to perfumes. Its essential oil is used in perfumes to add complexity and depth to the scent. Some perfumeries might use coriander essential oil in their perfumes, however, it is not always listed as an ingredient on the packaging or advertising. Brands like Jo Malone, Le Labo, Byredo, Diptyque, and other niche or artisanal perfumers might use coriander in their perfumes, but it is always better to check with the brands themselves.
Join Scentopia, Sentosa's latest tourist attraction wonderful orchid scent crafting, fragrance tour, bridal shower or corporate team building which includes perfume making onsite and offsite, beach activities and more. We also serve primary school learning journey, secondary students and pupil on industrial excursions. Know more about our orchids perfume bar or therapeutic orchid scents and other wellness aromas. Conatct Perfume workshop or book a scent crafting session here.