Orchids and Bees: A Fascinating Symbiotic Relationship!
The enchanting world of orchids and the bustling activities of bees have long captured the imagination of nature enthusiasts and scientists alike. These two seemingly distinct entities are intricately connected by a fascinating and vital relationship that has evolved over millions of years. Orchids and bees share a remarkable symbiotic bond that showcases the delicate balance of nature and the coevolutionary processes that shape the biodiversity of our planet.
Attracted by Fragrance and Color: Orchids, with their stunning array of colors and enchanting fragrances, have developed a variety of strategies to attract pollinators, including bees. Each orchid species has evolved specific adaptations to entice their targeted bee pollinators. Some orchids produce vibrant hues and unique patterns on their petals that mimic the appearance of female bees, tricking male bees into attempting to mate with them. During these amorous encounters, pollen is transferred from one orchid to another, facilitating cross-pollination and genetic diversity.
Other orchids emit powerful and alluring scents that mimic the pheromones released by female bees. These irresistible fragrances act as a beacon, guiding male bees to the orchids and inadvertently aiding in the process of pollination. The remarkable diversity of orchids and their specialized pollination strategies demonstrates the intricate dance between these flowers and their bee companions.
The Dance of Coevolution: The relationship between orchids and bees is a prime example of coevolution, where two species evolve in response to each other's needs and behaviors. Over time, as certain bee species developed a preference for specific orchid species, the orchids reciprocated by adapting their physical attributes and reproductive mechanisms to enhance their attractiveness to these particular pollinators.
Conversely, bees have also evolved morphological adaptations to effectively pollinate orchids. Some bees possess specialized structures, such as long tongues or legs, which enable them to reach deep into the intricate structures of certain orchid flowers and effectively collect and transport pollen. The successful pollination of orchids by bees is crucial for the reproduction and survival of both species, exemplifying the interdependence of life in nature.
Nectar as a Reward: One of the most critical aspects of the relationship between orchids and bees is the reward system. Orchids often produce nectar, a sweet liquid, as an enticement to visiting bees. Nectar serves as a valuable energy source for bees, providing them with essential nutrients and sustenance during their foraging activities. In return for this nutritious reward, bees inadvertently facilitate the pollination process as they move from one orchid to another in search of nectar.
Specialized Partnerships: Within the realm of orchids and bees, some relationships have become exceptionally specialized. Certain orchids have evolved to accommodate only one specific bee species as their primary pollinator. Similarly, certain bee species have become solely reliant on specific orchid species for their nectar and pollen sources. This high level of specialization is a testament to the intricate nature of coevolution and the intimate ties that exist between these plants and insects.
The Importance of Orchid-Bee Relationships: The orchid-bee relationship is not only captivating from a biological perspective but also plays a crucial role in the ecological balance of the habitats they inhabit. As important pollinators, bees facilitate the reproduction of orchids and contribute to the overall health and diversity of plant populations. Orchids, in turn, provide bees with essential food resources, contributing to the well-being of bee populations and the ecosystem at large.
Furthermore, these intricate relationships highlight the delicate balance of nature and underscore the importance of conserving both orchids and bees. Orchids, with their astonishing diversity and unique adaptations, are vulnerable to habitat loss and environmental changes. Similarly, bees face numerous threats, including habitat destruction, pesticides, and climate change, which could significantly impact their ability to pollinate orchids and other plant species.
In conclusion, the mesmerizing relationship between orchids and bees serves as a testament to the wonders of the natural world and the intricacies of coevolution. Orchids, with their captivating beauty and alluring fragrances, have evolved an array of specialized strategies to attract and rely on various bee species for pollination. In turn, bees have adapted their behaviors and physical traits to effectively forage and pollinate orchids. This interdependence highlights the essential role that both orchids and bees play in maintaining the biodiversity and ecological balance of their habitats. Understanding and preserving these relationships are crucial in fostering a sustainable and harmonious coexistence with nature.
The enchanting world of orchids and the bustling activities of bees have long captured the imagination of nature enthusiasts and scientists alike. These two seemingly distinct entities are intricately connected by a fascinating and vital relationship that has evolved over millions of years. Orchids and bees share a remarkable symbiotic bond that showcases the delicate balance of nature and the coevolutionary processes that shape the biodiversity of our planet.
Attracted by Fragrance and Color: Orchids, with their stunning array of colors and enchanting fragrances, have developed a variety of strategies to attract pollinators, including bees. Each orchid species has evolved specific adaptations to entice their targeted bee pollinators. Some orchids produce vibrant hues and unique patterns on their petals that mimic the appearance of female bees, tricking male bees into attempting to mate with them. During these amorous encounters, pollen is transferred from one orchid to another, facilitating cross-pollination and genetic diversity.
Other orchids emit powerful and alluring scents that mimic the pheromones released by female bees. These irresistible fragrances act as a beacon, guiding male bees to the orchids and inadvertently aiding in the process of pollination. The remarkable diversity of orchids and their specialized pollination strategies demonstrates the intricate dance between these flowers and their bee companions.
The Dance of Coevolution: The relationship between orchids and bees is a prime example of coevolution, where two species evolve in response to each other's needs and behaviors. Over time, as certain bee species developed a preference for specific orchid species, the orchids reciprocated by adapting their physical attributes and reproductive mechanisms to enhance their attractiveness to these particular pollinators.
Conversely, bees have also evolved morphological adaptations to effectively pollinate orchids. Some bees possess specialized structures, such as long tongues or legs, which enable them to reach deep into the intricate structures of certain orchid flowers and effectively collect and transport pollen. The successful pollination of orchids by bees is crucial for the reproduction and survival of both species, exemplifying the interdependence of life in nature.
Nectar as a Reward: One of the most critical aspects of the relationship between orchids and bees is the reward system. Orchids often produce nectar, a sweet liquid, as an enticement to visiting bees. Nectar serves as a valuable energy source for bees, providing them with essential nutrients and sustenance during their foraging activities. In return for this nutritious reward, bees inadvertently facilitate the pollination process as they move from one orchid to another in search of nectar.
Specialized Partnerships: Within the realm of orchids and bees, some relationships have become exceptionally specialized. Certain orchids have evolved to accommodate only one specific bee species as their primary pollinator. Similarly, certain bee species have become solely reliant on specific orchid species for their nectar and pollen sources. This high level of specialization is a testament to the intricate nature of coevolution and the intimate ties that exist between these plants and insects.
The Importance of Orchid-Bee Relationships: The orchid-bee relationship is not only captivating from a biological perspective but also plays a crucial role in the ecological balance of the habitats they inhabit. As important pollinators, bees facilitate the reproduction of orchids and contribute to the overall health and diversity of plant populations. Orchids, in turn, provide bees with essential food resources, contributing to the well-being of bee populations and the ecosystem at large.
Furthermore, these intricate relationships highlight the delicate balance of nature and underscore the importance of conserving both orchids and bees. Orchids, with their astonishing diversity and unique adaptations, are vulnerable to habitat loss and environmental changes. Similarly, bees face numerous threats, including habitat destruction, pesticides, and climate change, which could significantly impact their ability to pollinate orchids and other plant species.
In conclusion, the mesmerizing relationship between orchids and bees serves as a testament to the wonders of the natural world and the intricacies of coevolution. Orchids, with their captivating beauty and alluring fragrances, have evolved an array of specialized strategies to attract and rely on various bee species for pollination. In turn, bees have adapted their behaviors and physical traits to effectively forage and pollinate orchids. This interdependence highlights the essential role that both orchids and bees play in maintaining the biodiversity and ecological balance of their habitats. Understanding and preserving these relationships are crucial in fostering a sustainable and harmonious coexistence with nature.
To experience augmented reality, please open the Facebook-app using QR code and point to the image below
Orchids, with their stunning beauty and intricate structures, have mastered the art of attracting pollinators through an array of ingenious strategies. One of the primary tactics employed by orchids is to offer rewards to entice their pollinators. Nectar, a sugary liquid secreted by the flower, is the enticing treat that beckons insects and other animals to visit the orchid.
As the pollinator approaches the orchid to feed on the nectar, it inadvertently brushes against the flower's reproductive organs, picking up pollen in the process. When the pollinator moves on to another flower of the same orchid species to seek more nectar, it transfers the collected pollen onto the stigma (the female reproductive part) of the new flower. This process, known as pollination, is crucial for fertilization and the production of seeds.
The remarkable aspect of this relationship lies in its specificity. Some orchids form exclusive partnerships with particular pollinators, and these relationships are often finely tuned for optimal effectiveness. One such example is the intriguing bond between the Christmas star orchid (Angraecum sesquipedale) and the African hawkmoth (Xanthopan morganii praedicta).
The flowers of the Christmas star orchid boast an exceptionally long nectar-tube, a structure resembling a straw-like tube. Only the African hawkmoth, with its impressively long proboscis, possesses the perfect tool to reach the nectar deep within the orchid's flower. As the moth feeds, it inevitably collects pollen from the flower's anthers (the male reproductive structures). When the African hawkmoth then visits another Christmas star orchid, it transfers the gathered pollen to the stigma of the new flower, initiating the process of fertilization.
This exclusive relationship between the Christmas star orchid and the African hawkmoth highlights the astonishing coevolution between certain orchid species and their specialized pollinators. Over time, these unique partnerships have evolved to ensure successful reproduction for both the orchids and their pollinators.
By offering rewards such as nectar, orchids have perfected the art of enticing their pollinators, ensuring the continuation of their species. The specific adaptations, like the long nectar-tube of the Christmas star orchid and the matching proboscis of the African hawkmoth, exemplify nature's intricate designs and the marvels of natural selection.
In conclusion, the relationship between orchids and their pollinators exemplifies the exquisite balance and coexistence in the natural world. Orchids, with their sneaky tricks and alluring rewards, have managed to forge intimate connections with specific pollinators, ensuring the successful reproduction and perpetuation of their diverse and magnificent species. The intricate dance between orchids and their pollinators serves as a testament to the wonders of nature's strategies and the astounding beauty found in the floral kingdom. Through their captivating and ingenious methods, orchids continue to fascinate and captivate observers, reminding us of the rich tapestry of life that surrounds us.
As the pollinator approaches the orchid to feed on the nectar, it inadvertently brushes against the flower's reproductive organs, picking up pollen in the process. When the pollinator moves on to another flower of the same orchid species to seek more nectar, it transfers the collected pollen onto the stigma (the female reproductive part) of the new flower. This process, known as pollination, is crucial for fertilization and the production of seeds.
The remarkable aspect of this relationship lies in its specificity. Some orchids form exclusive partnerships with particular pollinators, and these relationships are often finely tuned for optimal effectiveness. One such example is the intriguing bond between the Christmas star orchid (Angraecum sesquipedale) and the African hawkmoth (Xanthopan morganii praedicta).
The flowers of the Christmas star orchid boast an exceptionally long nectar-tube, a structure resembling a straw-like tube. Only the African hawkmoth, with its impressively long proboscis, possesses the perfect tool to reach the nectar deep within the orchid's flower. As the moth feeds, it inevitably collects pollen from the flower's anthers (the male reproductive structures). When the African hawkmoth then visits another Christmas star orchid, it transfers the gathered pollen to the stigma of the new flower, initiating the process of fertilization.
This exclusive relationship between the Christmas star orchid and the African hawkmoth highlights the astonishing coevolution between certain orchid species and their specialized pollinators. Over time, these unique partnerships have evolved to ensure successful reproduction for both the orchids and their pollinators.
By offering rewards such as nectar, orchids have perfected the art of enticing their pollinators, ensuring the continuation of their species. The specific adaptations, like the long nectar-tube of the Christmas star orchid and the matching proboscis of the African hawkmoth, exemplify nature's intricate designs and the marvels of natural selection.
In conclusion, the relationship between orchids and their pollinators exemplifies the exquisite balance and coexistence in the natural world. Orchids, with their sneaky tricks and alluring rewards, have managed to forge intimate connections with specific pollinators, ensuring the successful reproduction and perpetuation of their diverse and magnificent species. The intricate dance between orchids and their pollinators serves as a testament to the wonders of nature's strategies and the astounding beauty found in the floral kingdom. Through their captivating and ingenious methods, orchids continue to fascinate and captivate observers, reminding us of the rich tapestry of life that surrounds us.
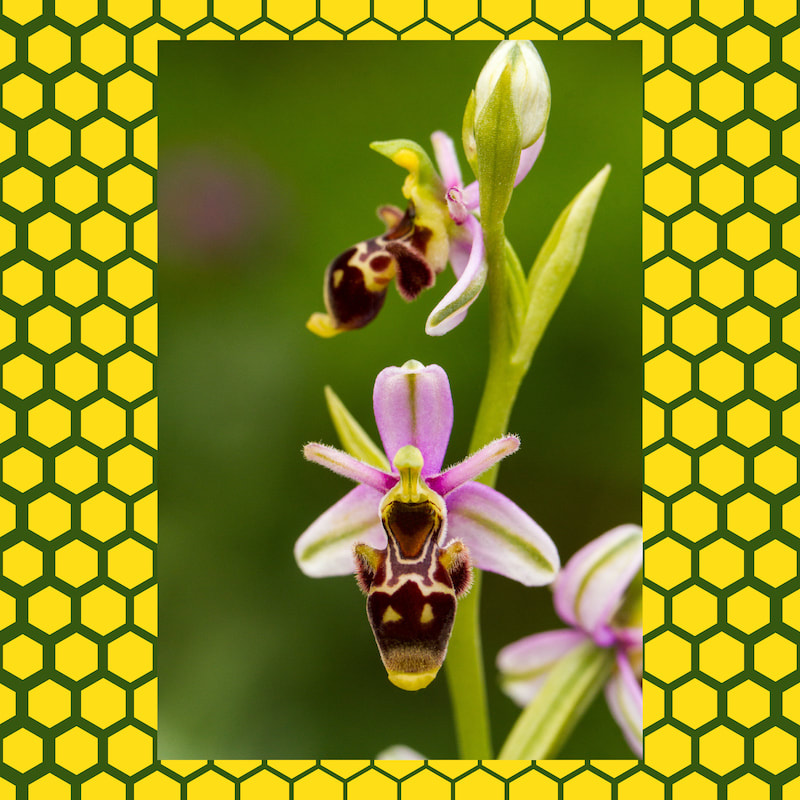
Deception is a fascinating and ingenious strategy employed by certain orchid species to attract their pollinators. Orchids that utilize this deceptive tactic have evolved to mimic the appearance and behavior of specific insects, often bees and wasps, in order to lure their unsuspecting pollinators into a unique relationship.
One remarkable example of deceptive orchids is the Bee orchid (Ophrys apifera). This captivating flower possesses a large lip-shaped petal, known as the labellum, which closely resembles the appearance of a female solitary bee from the species Eucera. The deceptive labellum is exquisitely designed to mimic the exact shape, color, and texture of the female bee, creating a remarkably convincing visual illusion.
When a male solitary bee comes across the Bee orchid, it perceives the flower as a potential mate and is tricked into attempting to mate with it. As the male bee gets close to the deceptive labellum, pollen grains from the flower attach themselves to the bee's body. Believing it has successfully "mated," the male bee then moves on to search for other female bees.
During subsequent mating attempts with real female bees, the pollen collected from the Bee orchid is transferred to the female's reproductive structures, effectively pollinating the flower. This is a clever and strategic method that ensures the Bee orchid's pollen is efficiently delivered to other flowers of the same species, promoting successful fertilization and seed production.
The deception used by the Bee orchid is a remarkable example of the coevolution between orchids and their pollinators. Over time, the orchids have evolved to imitate the appearance and behavior of specific pollinators, exploiting the instincts of these insects for their own reproductive benefit.
The phenomenon of deceptive orchids exemplifies nature's remarkable adaptability and the fascinating ways in which plants have evolved to secure their survival. Through their remarkable mimicry and deceitful strategies, these orchids have become masters of manipulating the behavior of their pollinators, ultimately ensuring the perpetuation of their species.
The intricate dance between deceptive orchids and their unwitting pollinators is a testament to the complexity of the natural world and the remarkable relationships that exist within it. Orchids, with their deceptive allure, continue to captivate and intrigue researchers and nature enthusiasts alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate and ingenious mechanisms that drive the perpetuation of life in the diverse and enchanting world of orchids.
One remarkable example of deceptive orchids is the Bee orchid (Ophrys apifera). This captivating flower possesses a large lip-shaped petal, known as the labellum, which closely resembles the appearance of a female solitary bee from the species Eucera. The deceptive labellum is exquisitely designed to mimic the exact shape, color, and texture of the female bee, creating a remarkably convincing visual illusion.
When a male solitary bee comes across the Bee orchid, it perceives the flower as a potential mate and is tricked into attempting to mate with it. As the male bee gets close to the deceptive labellum, pollen grains from the flower attach themselves to the bee's body. Believing it has successfully "mated," the male bee then moves on to search for other female bees.
During subsequent mating attempts with real female bees, the pollen collected from the Bee orchid is transferred to the female's reproductive structures, effectively pollinating the flower. This is a clever and strategic method that ensures the Bee orchid's pollen is efficiently delivered to other flowers of the same species, promoting successful fertilization and seed production.
The deception used by the Bee orchid is a remarkable example of the coevolution between orchids and their pollinators. Over time, the orchids have evolved to imitate the appearance and behavior of specific pollinators, exploiting the instincts of these insects for their own reproductive benefit.
The phenomenon of deceptive orchids exemplifies nature's remarkable adaptability and the fascinating ways in which plants have evolved to secure their survival. Through their remarkable mimicry and deceitful strategies, these orchids have become masters of manipulating the behavior of their pollinators, ultimately ensuring the perpetuation of their species.
The intricate dance between deceptive orchids and their unwitting pollinators is a testament to the complexity of the natural world and the remarkable relationships that exist within it. Orchids, with their deceptive allure, continue to captivate and intrigue researchers and nature enthusiasts alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate and ingenious mechanisms that drive the perpetuation of life in the diverse and enchanting world of orchids.
Orchids, with their diverse and ingenious pollination strategies, never fail to surprise us with their remarkable adaptations in the natural world. Among the various tactics employed by these enchanting blooms, one of the most fascinating is their use of traps to achieve successful pollination.
The Hammer orchids (Drakaea spp.) exemplify this intriguing approach. These orchids have developed a remarkable relationship with Thynnine wasps, which play a crucial role in their pollination process. The labellum, or lip, of the Hammer orchid flowers has evolved to closely resemble a female wasp in both appearance and scent, effectively deceiving male wasps into thinking they have found a potential mate.
The fascinating aspect of this trap lies in the unique mechanism that the Hammer orchid employs. When a male wasp attempts to mate with the flower, the labellum of the orchid swiftly and cleverly swings over, effectively flipping the wasp upside down and directly onto the stigma of the flower. This precise placement ensures that the pollen load from the wasp adheres to the stigma, facilitating pollination.
In this extraordinary interaction, the Hammer orchids take advantage of the male wasps' instincts, successfully trapping them for the vital transfer of pollen. By imitating the appearance and scent of a female wasp, the orchids capitalize on the wasps' natural behavior, ensuring effective pollination through their cunning trap.
This unique pollination strategy showcases the incredible co-evolution between orchids and their pollinators, illustrating the remarkable interplay between plants and insects in the natural world. Orchids, as one of the oldest families of flowering plants, have evolved a myriad of techniques to ensure their survival and reproduction, and their trap-like pollination is a testament to their adaptability and ingenuity.
The intricate and specialized relationships between orchids and their pollinators provide a captivating glimpse into the intricacies of the natural world. Each orchid species has honed its pollination strategy over millennia, resulting in a dazzling array of captivating and diverse blooms that continue to mesmerize botanists, entomologists, and nature enthusiasts alike.
As we continue to explore the fascinating world of orchids and their pollination tactics, we gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of the natural world, where plants and animals coexist in harmony, shaping and influencing each other's evolutionary paths in a dance of life and survival. Orchids, with their alluring traps, serve as a living testament to the marvels of nature's ingenuity and the wonders that await discovery in the vast and diverse realms of flora and fauna.
The Hammer orchids (Drakaea spp.) exemplify this intriguing approach. These orchids have developed a remarkable relationship with Thynnine wasps, which play a crucial role in their pollination process. The labellum, or lip, of the Hammer orchid flowers has evolved to closely resemble a female wasp in both appearance and scent, effectively deceiving male wasps into thinking they have found a potential mate.
The fascinating aspect of this trap lies in the unique mechanism that the Hammer orchid employs. When a male wasp attempts to mate with the flower, the labellum of the orchid swiftly and cleverly swings over, effectively flipping the wasp upside down and directly onto the stigma of the flower. This precise placement ensures that the pollen load from the wasp adheres to the stigma, facilitating pollination.
In this extraordinary interaction, the Hammer orchids take advantage of the male wasps' instincts, successfully trapping them for the vital transfer of pollen. By imitating the appearance and scent of a female wasp, the orchids capitalize on the wasps' natural behavior, ensuring effective pollination through their cunning trap.
This unique pollination strategy showcases the incredible co-evolution between orchids and their pollinators, illustrating the remarkable interplay between plants and insects in the natural world. Orchids, as one of the oldest families of flowering plants, have evolved a myriad of techniques to ensure their survival and reproduction, and their trap-like pollination is a testament to their adaptability and ingenuity.
The intricate and specialized relationships between orchids and their pollinators provide a captivating glimpse into the intricacies of the natural world. Each orchid species has honed its pollination strategy over millennia, resulting in a dazzling array of captivating and diverse blooms that continue to mesmerize botanists, entomologists, and nature enthusiasts alike.
As we continue to explore the fascinating world of orchids and their pollination tactics, we gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of the natural world, where plants and animals coexist in harmony, shaping and influencing each other's evolutionary paths in a dance of life and survival. Orchids, with their alluring traps, serve as a living testament to the marvels of nature's ingenuity and the wonders that await discovery in the vast and diverse realms of flora and fauna.
Join Scentopia's wonderful orchid scent crafting, fragrance tour, bridal shower or corporate team building which includes perfume making onsite and offsite, beach activities and more. We also serve primary school learning journey, secondary students and pupil on industrial excursions. Know more about our orchids perfume bar or therapeutic orchid scents and other wellness aromas. Conatct Perfume workshop or book a scent crafting session here.