The evolution of aroma machines and fragrance factories has been a fascinating journey that spans centuries and is deeply intertwined with human civilization's progress. From the ancient use of incense to the modern-day sophisticated aroma machines, the pursuit of pleasant scents has played a significant role in enhancing our living spaces, industries, and overall well-being.
The use of fragrances and pleasant scents dates back to ancient times. In early human history, people discovered the aromatic properties of various natural substances such as flowers, herbs, resins, and spices. These substances were burnt as incense in religious ceremonies, used in perfumes, and infused into oils for medicinal and therapeutic purposes. The ancient civilizations of Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, and India all valued and incorporated the use of fragrances in their cultural practices.
As human societies advanced, so did their methods of extracting and preserving fragrances. The Middle Ages saw the rise of the perfume industry in Europe, with techniques for distillation and enfleurage being developed. Enfleurage involved placing fragrant flowers on fats, allowing their scents to be absorbed and preserved in the oils. These techniques laid the foundation for the commercial production of fragrances and the establishment of perfume factories.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about significant advancements in technology and manufacturing processes, including fragrance production. With the introduction of steam engines and chemical processes, perfume factories could now produce fragrances on a larger scale and at a more affordable cost. The emergence of synthetic fragrance compounds in the late 19th century further revolutionized the industry, providing perfumers with an extensive array of new scents to work with.
In the early 20th century, the fragrance industry witnessed a surge in popularity and innovation. Iconic perfume houses were established, creating timeless fragrances that are still revered today. Perfume factories became hubs of creativity, employing skilled perfumers and chemists to create unique and captivating scents. The establishment of luxury fragrance brands and the rise of celebrity-endorsed perfumes further boosted the industry's growth and global reach.
As technology continued to advance, so did the methods of delivering fragrances to consumers. Aroma machines, also known as scent diffusers or fragrance dispensers, emerged as a popular means of diffusing scents in enclosed spaces such as homes, offices, hotels, and retail environments. These machines offered a more controlled and consistent way of dispersing fragrances, allowing for customizable scent experiences based on various factors such as time of day, ambiance, and customer preferences.
Modern aroma machines utilize advanced technologies such as ultrasonic nebulizers, cold air diffusion, and heat evaporation to disperse fragrance molecules effectively. Some aroma machines are equipped with smart capabilities, allowing for remote control and programmable scent schedules. Businesses have embraced aroma marketing as a powerful tool to create immersive and memorable customer experiences, influencing purchasing decisions and brand perception.
Furthermore, the fragrance industry has expanded beyond personal care and home use. It has found applications in various sectors, including hospitality, healthcare, and even virtual reality. The use of scents in hospitals to promote relaxation and healing, in hotels to create distinctive atmospheres, and in virtual reality simulations to enhance the immersive experience exemplifies the versatility and growing importance of fragrances in different domains.
In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in natural and sustainable fragrance solutions. Consumers are seeking eco-friendly and non-toxic scents, driving fragrance companies to explore environmentally friendly ingredients and packaging. The blending of ancient knowledge with modern innovation has led to the development of botanical-based perfumes and essential oil-based fragrance alternatives.
In conclusion, the evolution of aroma machines and fragrance factories is a testament to the enduring human fascination with pleasant scents and the desire to create uplifting and transformative olfactory experiences. From the early use of incense in ancient rituals to the sophisticated aroma machines and advanced fragrance production processes of today, the fragrance industry continues to evolve, innovate, and captivate our senses. As technology and consumer preferences continue to evolve, the fragrance industry will undoubtedly adapt, offering new possibilities and opportunities to enrich our lives with delightful scents.
The use of fragrances and pleasant scents dates back to ancient times. In early human history, people discovered the aromatic properties of various natural substances such as flowers, herbs, resins, and spices. These substances were burnt as incense in religious ceremonies, used in perfumes, and infused into oils for medicinal and therapeutic purposes. The ancient civilizations of Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, and India all valued and incorporated the use of fragrances in their cultural practices.
As human societies advanced, so did their methods of extracting and preserving fragrances. The Middle Ages saw the rise of the perfume industry in Europe, with techniques for distillation and enfleurage being developed. Enfleurage involved placing fragrant flowers on fats, allowing their scents to be absorbed and preserved in the oils. These techniques laid the foundation for the commercial production of fragrances and the establishment of perfume factories.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about significant advancements in technology and manufacturing processes, including fragrance production. With the introduction of steam engines and chemical processes, perfume factories could now produce fragrances on a larger scale and at a more affordable cost. The emergence of synthetic fragrance compounds in the late 19th century further revolutionized the industry, providing perfumers with an extensive array of new scents to work with.
In the early 20th century, the fragrance industry witnessed a surge in popularity and innovation. Iconic perfume houses were established, creating timeless fragrances that are still revered today. Perfume factories became hubs of creativity, employing skilled perfumers and chemists to create unique and captivating scents. The establishment of luxury fragrance brands and the rise of celebrity-endorsed perfumes further boosted the industry's growth and global reach.
As technology continued to advance, so did the methods of delivering fragrances to consumers. Aroma machines, also known as scent diffusers or fragrance dispensers, emerged as a popular means of diffusing scents in enclosed spaces such as homes, offices, hotels, and retail environments. These machines offered a more controlled and consistent way of dispersing fragrances, allowing for customizable scent experiences based on various factors such as time of day, ambiance, and customer preferences.
Modern aroma machines utilize advanced technologies such as ultrasonic nebulizers, cold air diffusion, and heat evaporation to disperse fragrance molecules effectively. Some aroma machines are equipped with smart capabilities, allowing for remote control and programmable scent schedules. Businesses have embraced aroma marketing as a powerful tool to create immersive and memorable customer experiences, influencing purchasing decisions and brand perception.
Furthermore, the fragrance industry has expanded beyond personal care and home use. It has found applications in various sectors, including hospitality, healthcare, and even virtual reality. The use of scents in hospitals to promote relaxation and healing, in hotels to create distinctive atmospheres, and in virtual reality simulations to enhance the immersive experience exemplifies the versatility and growing importance of fragrances in different domains.
In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in natural and sustainable fragrance solutions. Consumers are seeking eco-friendly and non-toxic scents, driving fragrance companies to explore environmentally friendly ingredients and packaging. The blending of ancient knowledge with modern innovation has led to the development of botanical-based perfumes and essential oil-based fragrance alternatives.
In conclusion, the evolution of aroma machines and fragrance factories is a testament to the enduring human fascination with pleasant scents and the desire to create uplifting and transformative olfactory experiences. From the early use of incense in ancient rituals to the sophisticated aroma machines and advanced fragrance production processes of today, the fragrance industry continues to evolve, innovate, and captivate our senses. As technology and consumer preferences continue to evolve, the fragrance industry will undoubtedly adapt, offering new possibilities and opportunities to enrich our lives with delightful scents.
To experience augmented reality, please open the Facebook-app using QR code and point to the image below
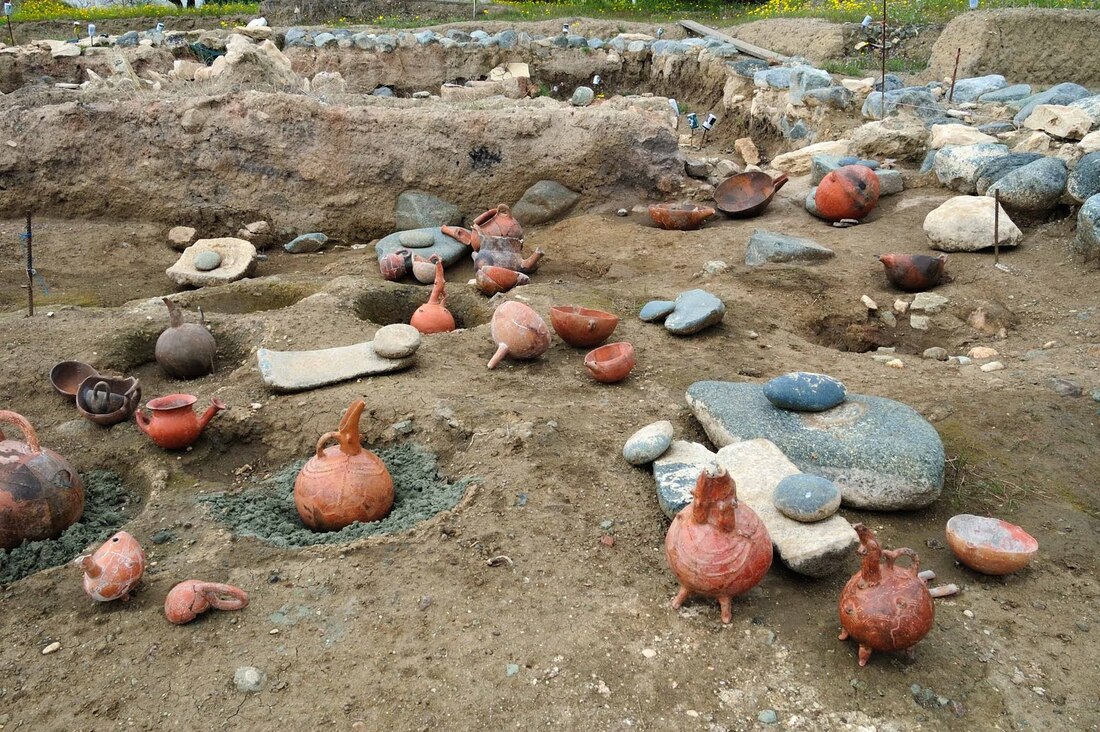
Perfumery has a rich and ancient history that spans across civilizations and cultures. The oldest evidence of perfume manufacturing was discovered on the island of Cyprus, dating back 4,000 years during the Bronze Age. This ancient factory covered a vast surface area of over 4,000m², indicating that perfume production was conducted on an industrial scale even in antiquity.
In the Indian subcontinent, perfumery also thrived in the ancient Indus civilization, which existed from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE. The distillation of Ittar, a traditional form of perfume made from natural ingredients, was mentioned in Hindu Ayurvedic texts such as the Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita. The art of perfume-making was highly regarded and practiced by skilled artisans who carefully extracted aromatic compounds from flowers, roots, herbs, and other natural sources.
The ancient Egyptians and Mesopotamians were also known for their early expertise in perfume-making. Hieroglyphics found in Egyptian tombs and ancient texts from Mesopotamia provide evidence that perfume and perfumery were integral to their cultures. The first perfumers were often religious figures, such as Egyptian priests, who used aromatic resins to sweeten the smell of sacrificial offerings and ceremonies.
One remarkable figure in the history of perfumery is Tapputi, the world's first recorded chemist, who lived around 1200 BCE in Babylonian Mesopotamia. Her existence was documented on a Cuneiform tablet, which highlights her role as a skilled perfume maker. Tapputi's contributions to the field of perfumery demonstrate that women have been involved in the science and art of fragrance creation since ancient times.
Throughout history, perfumery continued to evolve and expand its reach to various parts of the world. Ancient trade routes, such as the Silk Road, facilitated the exchange of aromatic ingredients, allowing cultures to experiment with new scents and techniques. As societies advanced, so did the methods of extracting and preserving fragrances, leading to the establishment of perfume houses, skilled perfumers, and fragrance factories.
In the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, perfumery experienced a resurgence in Europe, with the development of innovative techniques such as enfleurage and distillation. The Renaissance period marked a significant period of exploration and discovery, leading to the incorporation of exotic scents from distant lands into perfumes.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about transformative changes to perfumery. Technological advancements, such as steam engines and chemical processes, enabled large-scale production of fragrances and the synthesis of new aroma compounds. This era also saw the rise of iconic perfume houses that created timeless and beloved fragrances.
Today, perfumery has become a sophisticated industry that combines art, science, and technology. The fragrance market offers an extensive array of perfumes, colognes, and personal care products to suit diverse tastes and preferences. Perfume factories and laboratories employ skilled perfumers, chemists, and scent experts to create unique and captivating scents that cater to the modern consumer's desires.
Moreover, the quest for natural and sustainable fragrances has gained prominence in recent years. Consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly and non-toxic fragrance options, leading perfumers and manufacturers to explore environmentally friendly ingredients and packaging.
In conclusion, the history of perfumery is a testament to humanity's enduring fascination with scents and the desire to create aromatic experiences that delight our senses. From ancient civilizations to modern perfume factories, the art and science of perfumery have evolved, leaving an indelible mark on human culture and society. Perfumes continue to be cherished as a form of self-expression, luxury, and sensory pleasure, connecting people across time and space through the shared experience of delightful aromas.
In the Indian subcontinent, perfumery also thrived in the ancient Indus civilization, which existed from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE. The distillation of Ittar, a traditional form of perfume made from natural ingredients, was mentioned in Hindu Ayurvedic texts such as the Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita. The art of perfume-making was highly regarded and practiced by skilled artisans who carefully extracted aromatic compounds from flowers, roots, herbs, and other natural sources.
The ancient Egyptians and Mesopotamians were also known for their early expertise in perfume-making. Hieroglyphics found in Egyptian tombs and ancient texts from Mesopotamia provide evidence that perfume and perfumery were integral to their cultures. The first perfumers were often religious figures, such as Egyptian priests, who used aromatic resins to sweeten the smell of sacrificial offerings and ceremonies.
One remarkable figure in the history of perfumery is Tapputi, the world's first recorded chemist, who lived around 1200 BCE in Babylonian Mesopotamia. Her existence was documented on a Cuneiform tablet, which highlights her role as a skilled perfume maker. Tapputi's contributions to the field of perfumery demonstrate that women have been involved in the science and art of fragrance creation since ancient times.
Throughout history, perfumery continued to evolve and expand its reach to various parts of the world. Ancient trade routes, such as the Silk Road, facilitated the exchange of aromatic ingredients, allowing cultures to experiment with new scents and techniques. As societies advanced, so did the methods of extracting and preserving fragrances, leading to the establishment of perfume houses, skilled perfumers, and fragrance factories.
In the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, perfumery experienced a resurgence in Europe, with the development of innovative techniques such as enfleurage and distillation. The Renaissance period marked a significant period of exploration and discovery, leading to the incorporation of exotic scents from distant lands into perfumes.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about transformative changes to perfumery. Technological advancements, such as steam engines and chemical processes, enabled large-scale production of fragrances and the synthesis of new aroma compounds. This era also saw the rise of iconic perfume houses that created timeless and beloved fragrances.
Today, perfumery has become a sophisticated industry that combines art, science, and technology. The fragrance market offers an extensive array of perfumes, colognes, and personal care products to suit diverse tastes and preferences. Perfume factories and laboratories employ skilled perfumers, chemists, and scent experts to create unique and captivating scents that cater to the modern consumer's desires.
Moreover, the quest for natural and sustainable fragrances has gained prominence in recent years. Consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly and non-toxic fragrance options, leading perfumers and manufacturers to explore environmentally friendly ingredients and packaging.
In conclusion, the history of perfumery is a testament to humanity's enduring fascination with scents and the desire to create aromatic experiences that delight our senses. From ancient civilizations to modern perfume factories, the art and science of perfumery have evolved, leaving an indelible mark on human culture and society. Perfumes continue to be cherished as a form of self-expression, luxury, and sensory pleasure, connecting people across time and space through the shared experience of delightful aromas.
The history of perfumery in Europe is a fascinating journey that traces its roots back to the 14th century, influenced by Arabic knowledge and trade routes. The early introduction of perfumery to Europe can be attributed to interactions with the Arab world, where perfumery had already developed into an art form and a highly valued cultural tradition.
Arab traders and scholars played a crucial role in transmitting knowledge of perfumery to Europe through their extensive networks of trade and cultural exchange. As Europe engaged in various commercial and cultural interactions with the Arab world during the Middle Ages, it was introduced to the luxurious and captivating world of perfumes.
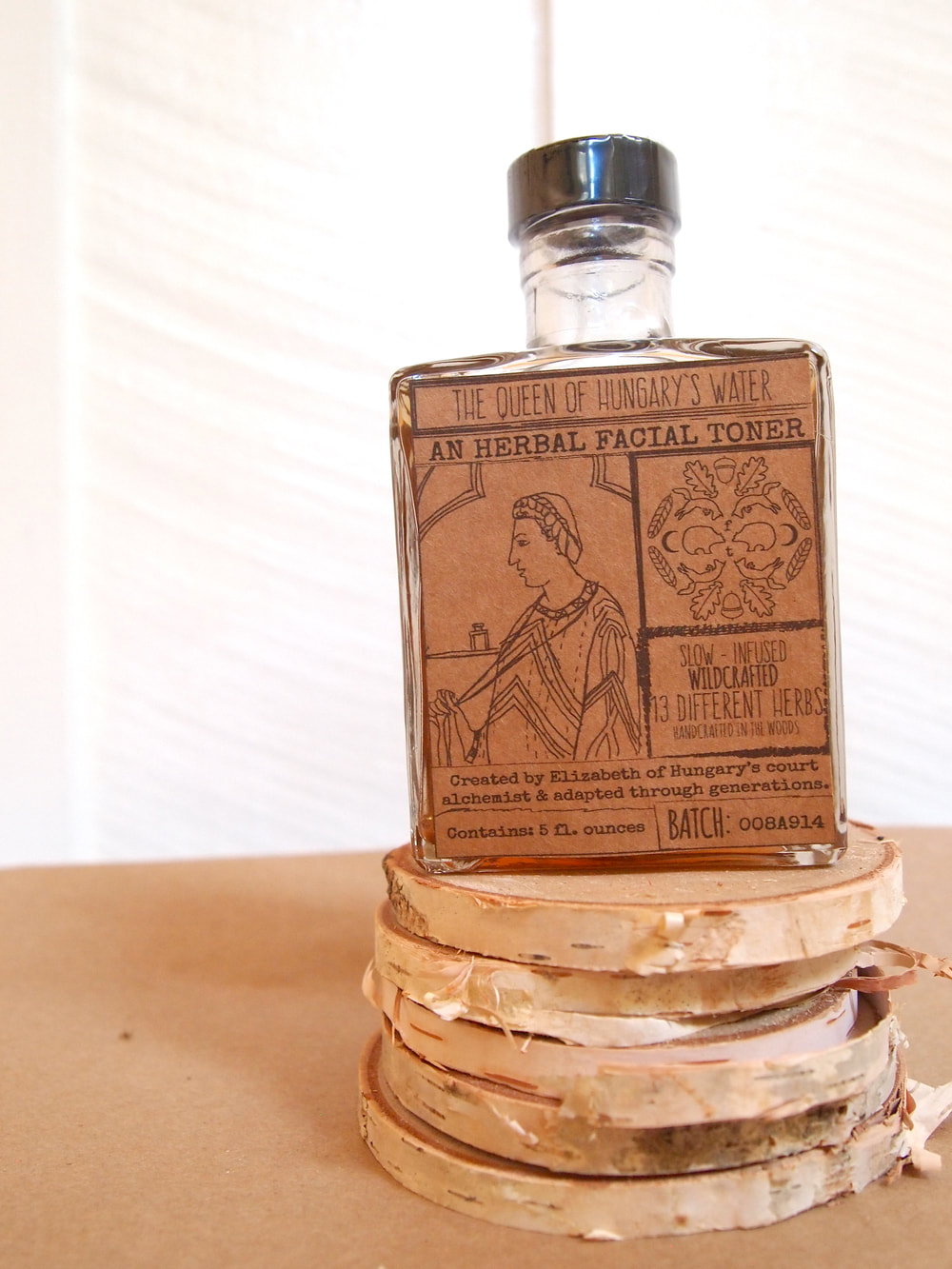
One significant event in the history of European perfumery was the creation of the first modern perfume known as Hungary Water. This iconic fragrance was made in 1370 at the request of Queen Elizabeth of Hungary. Hungary Water was a blend of scented oils suspended in an alcohol solution, creating a sophisticated and long-lasting fragrance. This innovation marked the beginning of a new era for perfumery in Europe, as it paved the way for the use of alcohol as a solvent for fragrances.
The popularity of Hungary Water quickly spread throughout Europe, and it became renowned for its rejuvenating and healing properties. It was used as a cosmetic and medicinal product, believed to have various therapeutic benefits. Hungary Water's success inspired other European regions to delve into the world of perfumery, leading to the emergence of various perfume workshops and artisans across the continent.
France soon emerged as the epicenter of perfume and cosmetic manufacture in Europe. The cultivation of flowers for their perfume essence had already begun in the 14th century, but it flourished into a major industry in the south of France, particularly in the region of Grasse. Grasse, with its favorable climate and fertile soil, became the heart of the European perfume industry and is now regarded as the world capital of perfume.
Grasse's abundance of fragrant flowers, such as roses, jasmine, lavender, and orange blossoms, provided an ideal environment for cultivating the essential oils needed for perfumes. The region's perfumers mastered the art of extracting and blending these aromatic essences to create exquisite and complex fragrances that captivated the senses.
During the Renaissance and subsequent centuries, French perfumers honed their craft and perfected the techniques of scent extraction, distillation, and blending. The French aristocracy and royal courts became avid patrons of perfumery, commissioning unique fragrances that reflected their status and refined tastes.
The 18th and 19th centuries witnessed significant advancements in perfumery, driven by the Industrial Revolution and the discovery of new aroma compounds. Innovations in chemistry allowed perfumers to synthesize fragrant molecules that were previously unattainable from natural sources. This era also marked the establishment of iconic perfume houses that are still renowned today for their timeless creations.
In the modern era, the art and science of perfumery continue to evolve, with advancements in technology, sustainability, and creative expression. Perfumers now have access to a vast array of natural and synthetic ingredients, enabling them to craft an extensive range of fragrances to suit diverse preferences and lifestyles.
The history of European perfumery is a testament to the enduring allure of scents and their profound impact on human culture and society. From the humble beginnings of Hungary Water to the opulent perfume houses of France, European perfumery has transcended time and borders to become a universal expression of luxury, beauty, and sensory pleasure. Today, the enchanting world of perfumes continues to inspire and enchant people worldwide, connecting us through the shared experience of delightful aromas and evoking memories and emotions that transcend time and place.
Arab traders and scholars played a crucial role in transmitting knowledge of perfumery to Europe through their extensive networks of trade and cultural exchange. As Europe engaged in various commercial and cultural interactions with the Arab world during the Middle Ages, it was introduced to the luxurious and captivating world of perfumes.
One significant event in the history of European perfumery was the creation of the first modern perfume known as Hungary Water. This iconic fragrance was made in 1370 at the request of Queen Elizabeth of Hungary. Hungary Water was a blend of scented oils suspended in an alcohol solution, creating a sophisticated and long-lasting fragrance. This innovation marked the beginning of a new era for perfumery in Europe, as it paved the way for the use of alcohol as a solvent for fragrances.
The popularity of Hungary Water quickly spread throughout Europe, and it became renowned for its rejuvenating and healing properties. It was used as a cosmetic and medicinal product, believed to have various therapeutic benefits. Hungary Water's success inspired other European regions to delve into the world of perfumery, leading to the emergence of various perfume workshops and artisans across the continent.
France soon emerged as the epicenter of perfume and cosmetic manufacture in Europe. The cultivation of flowers for their perfume essence had already begun in the 14th century, but it flourished into a major industry in the south of France, particularly in the region of Grasse. Grasse, with its favorable climate and fertile soil, became the heart of the European perfume industry and is now regarded as the world capital of perfume.
Grasse's abundance of fragrant flowers, such as roses, jasmine, lavender, and orange blossoms, provided an ideal environment for cultivating the essential oils needed for perfumes. The region's perfumers mastered the art of extracting and blending these aromatic essences to create exquisite and complex fragrances that captivated the senses.
During the Renaissance and subsequent centuries, French perfumers honed their craft and perfected the techniques of scent extraction, distillation, and blending. The French aristocracy and royal courts became avid patrons of perfumery, commissioning unique fragrances that reflected their status and refined tastes.
The 18th and 19th centuries witnessed significant advancements in perfumery, driven by the Industrial Revolution and the discovery of new aroma compounds. Innovations in chemistry allowed perfumers to synthesize fragrant molecules that were previously unattainable from natural sources. This era also marked the establishment of iconic perfume houses that are still renowned today for their timeless creations.
In the modern era, the art and science of perfumery continue to evolve, with advancements in technology, sustainability, and creative expression. Perfumers now have access to a vast array of natural and synthetic ingredients, enabling them to craft an extensive range of fragrances to suit diverse preferences and lifestyles.
The history of European perfumery is a testament to the enduring allure of scents and their profound impact on human culture and society. From the humble beginnings of Hungary Water to the opulent perfume houses of France, European perfumery has transcended time and borders to become a universal expression of luxury, beauty, and sensory pleasure. Today, the enchanting world of perfumes continues to inspire and enchant people worldwide, connecting us through the shared experience of delightful aromas and evoking memories and emotions that transcend time and place.
Join Scentopia, Sentosa's latest tourist attraction wonderful orchid scent crafting, fragrance tour, bridal shower or corporate team building which includes perfume making onsite and offsite, beach activities and more. We also serve primary school learning journey, secondary students and pupil on industrial excursions. Know more about our orchids perfume bar or therapeutic orchid scents and other wellness aromas. Conatct Perfume workshop or book a scent crafting session here.